Figure 1.
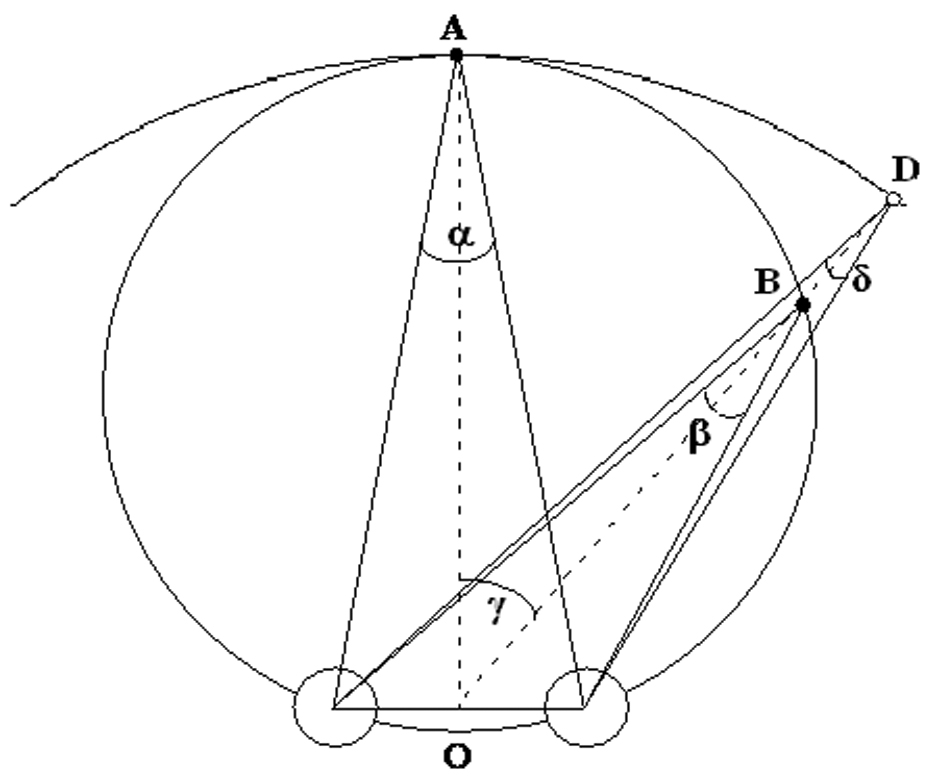
Plan view of iso-vergence circle (large complete circle), iso-accommodation circle (shown as an arc) and various azimuth angles. The two small circles represent the right and the left eye. The point A represents the spatial location that corresponds to matched stimuli for accommodation and convergence. α = convergence angle at point A (angle made by the intersection of two lines of sight), β = convergence angle at point B, and α = β along the iso-vergence circle. γ = lateral gaze angle. Note that at point D on the iso-accommodation circle, the convergence stimulus is lower than at point B by δ.
