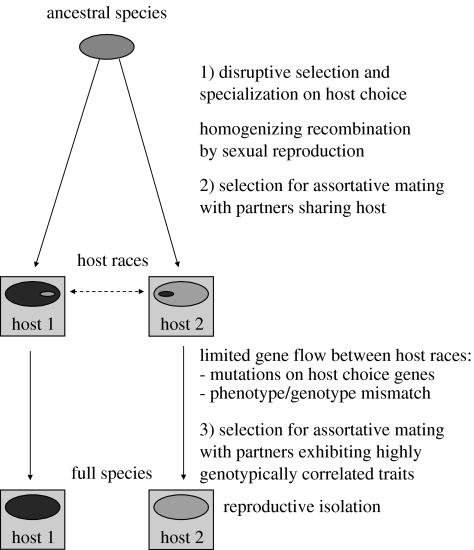
Figure 4.
Species are hypothesized to evolve sympatrically in two steps. First, there is disruptive selection for specialization on hosts. Two hypothetical hosts are represented by squares. Specialists in guilds are better than generalists at matching their host environment. They are also less susceptible to harmful mutations than are generalists (see text). Specialization is counter-selected by gene flow between host races mediated by mutations in host choice genes. Sexual recombination, including meiotic crossover, homogenizes genotypic variation. Host races may evolve by partial reproductive isolation if mate choice is restricted to those sharing the same host. When host races are established, selection favours mate choice based on traits that correlate broadly and strongly with the genotype. The result will be more complete reproductive isolation and sympatrically evolved species.