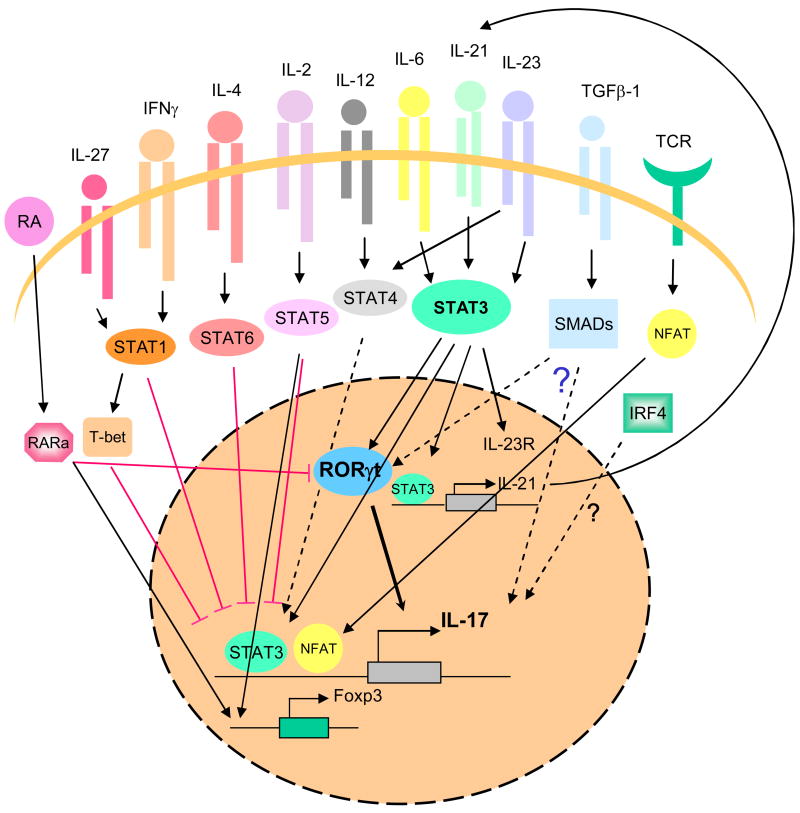
Figure 1. Signaling pathways and transcription factors that regulate Th17 differentiation.
In helper T cells, TCR stimulation activates NFAT, which likely directly regulates IL17 expression. Cytokines such IL-6, IL-21 and IL-23, activate STAT3, which also binds Il17a/f, and Il21 genes and controls Rorc and Il23r expression. TGFβ-1 signaling involves the activation of SMAD proteins. This cytokine acts in conjunction with STAT3 and Rorγt, although the mechanism through which TGFβ-1 promotes differentiation of Th17 cells is presently unknown. IRF4 is also a positive regulator of Th17 differentiation, how it acts is unclear.
Unsurprisingly, many factors inhibit Th17 differentiation. Retinoic acid, acting through its cognate receptors, downregulates IL-17 expression and upregulates Foxp3 expression. IL-2, IL-4, IFNγ and IL-27 activate STAT5, STAT6 and STAT1, respectively, also negatively regulate Il17a expression. Foxp3 also inhibits cytokine production.