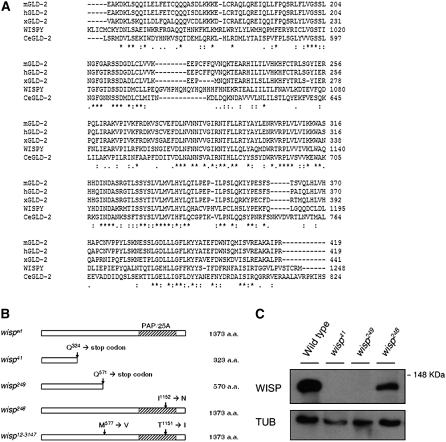
Figure 1.—
Wild-type and mutant protein sequences of WISP. (A) Amino acid sequence of the predicted PAP domain of WISP was aligned against those of GLD-2 proteins of C.elegans, Xenopus, humans, and mice. Identical or similar residues between the sequences are indicated with an asterisk or dot(s), respectively. (B) Schematic of wisp alleles. wisp41 and wisp249 have nonsense mutations in the coding region that result in truncated proteins of 323 aa and 570 aa, respectively. wisp248 has a point mutation at position 1152, resulting in a Ile-to-Asp change. wisp12-3147 has point mutations at positions 577 and 1151, which result in Met-to-Val and Thr-to-Ile substitutions, respectively. (C) Western blot analysis. Ovaries were dissected from wild-type, wisp41/wisp41, wisp248/wisp248, and wisp249/wisp249 females. Ovarian protein extracts were separated by SDS–PAGE, blotted, and probed with affinity-purified polyclonal anti-WISP directed against the 411 aa C-term part of the protein or with anti-α-tubulin (loading control; TUB). A protein of ∼140 kDa is detected in ovarian extracts of wild-type and wisp248/wisp248 females. This band is absent in ovarian extracts of wisp41/wisp41 and wisp249/wisp249 females.