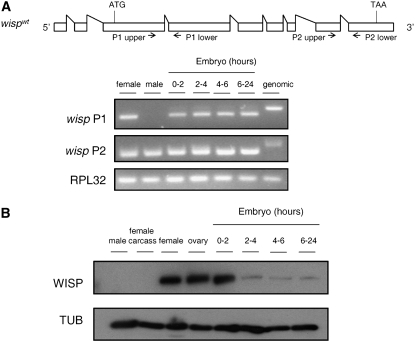
Figure 2.—
Presence of wisp transcripts and proteins. (A) Total RNAs were extracted from 3- to 4-day-old wild-type adult female and male flies or laid embryos of the indicated ages. mRNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA for PCR analysis. RPL32 primers were used as positive control. Two different sets of wisp primers shown in the context of the wisp mRNA as predicted in FlyBase (http://www.flybase.org) were used to detect wisp transcripts. A PCR product for wisp P1 is present in all samples examined except male cDNA. PCR products for both wisp P2 and RPL32 are present in all samples. (B) Ovaries were dissected from 3- to 4–day-old virgin females and the females' remaining somatic tissues were used as the female carcass sample. Total protein extracts from these two samples, wild-type adult flies and laid embryos of the indicated ages, were separated by SDS–PAGE, blotted, and probed for anti-WISP and anti-α-tubulin (TUB; loading control).