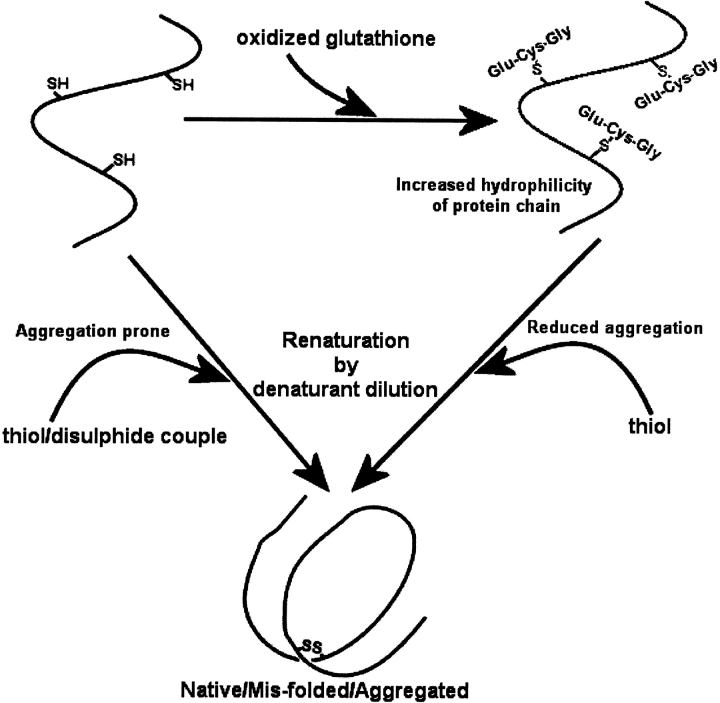
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of two routes for protein renaturation. Renaturation is possible via an aggregation-prone route by direct dilution from the denatured-reduced state, in the presence of a thiol/disulfide couple. Alternatively, renaturation can occur from a denatured mixed-disulfide state, in which the hydrophilicity of the denatured protein chains is increased by the addition of glutathione to the polypeptide prior to dilution. Glutathione is the tripeptide of glutamate–cysteine–glycine.