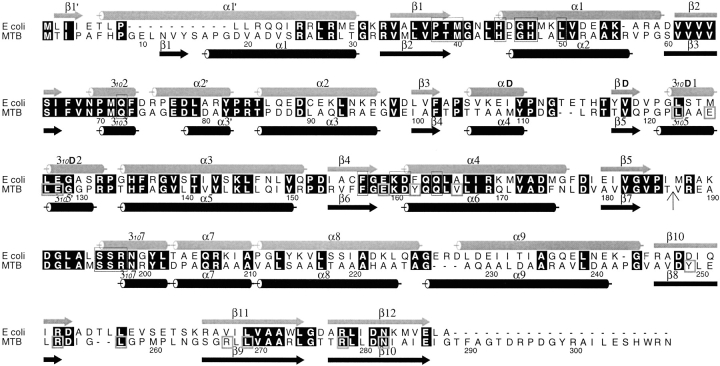
Figure 2.
Sequence alignment between the E. coli and M. tuberculosis PS proteins. The sequences were aligned with CLUSTALW (Thompson et al. 1994) and the figure was generated using ALSCRIPT (Barton 1993). Identical residues are highlighted in black. Helices and β-strands of the two structures are marked with cylinders and arrows, respectively. The secondary structure elements and numbering for the E. coli PS are from von Delft et al. (2001). Residues involved in binding of AMPCPP, pantoate, or pantoyl adenylate are boxed in thin lines, while those involved in interactions between N- and C-terminal domains are boxed in thick lines in the M. tuberculosis sequence. A vertical arrow marks the start of the C-terminal domain. All residues involved in binding of substrates and the reaction intermediate are conserved between two sequences, indicating that they have identical reaction mechanism. However, residues involved in domain interactions are not all conserved. See text for more details.