Figure 3.
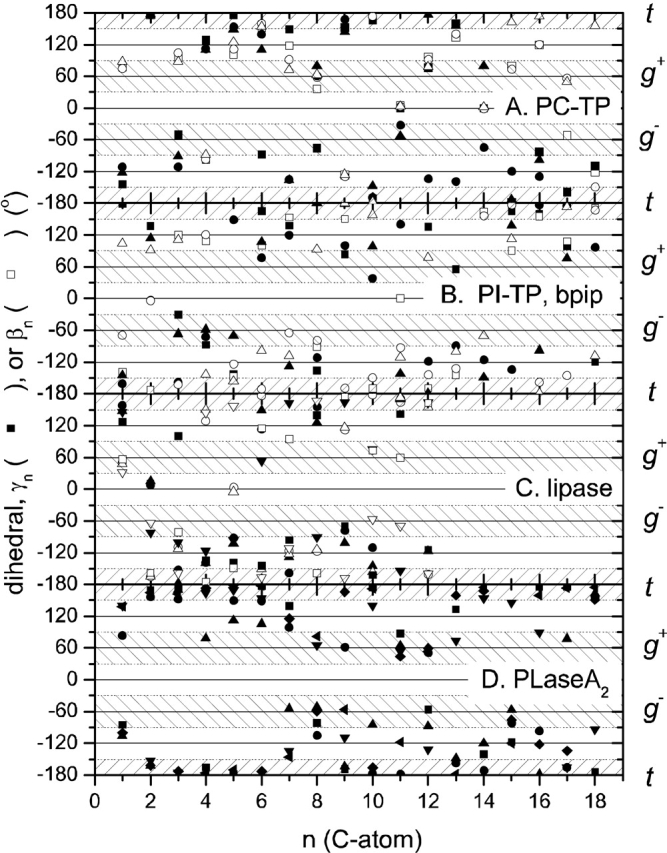
Torsion angles, Cn−3Cn−2Cn−1Cn, in the sn-1 (solid symbols) and the sn-2 (open symbols) chains of protein-bound phospholipids. A. Dilinoleoyl phosphatidylcholine (DLP; ▪,□) or 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine (CPL; •,○;▴,▵) bound to the human phosphatidylcholine transfer protein (PDB:1LNX, 1LN3; Roderick et al. 2002). B. Distearoyl phosphatidylcholine (PC2) bound to the α-isoform of rat phosphatidylinositol transfer protein (▪,□) (PDB:1FVZ; Yoder et al. 2001) or to the human bactericidal permeability-increasing protein (•,○;▴,▵) (PDB:1EWF; Kleiger et al. 2000). C. Dilauroyl phosphatidylcholine (PLC) bound to Th. lanuginosa lipase (▪,□; •,○;▴,▵) (PDB:1EIN; Brzozowski et al. 2000) or to human pancreatic lipase-procolipase complex (▾,▿) (PDB:1LPA; van Tilbeurgh et al. 1993). D. 1-O-octadecyl-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethyl methylsulphide (INB) bound to human synovial phospholipase A2 (PDB:1AYP; Oh 1995). Shapes of symbols are used to distinguish the individual lipids in each panel.
