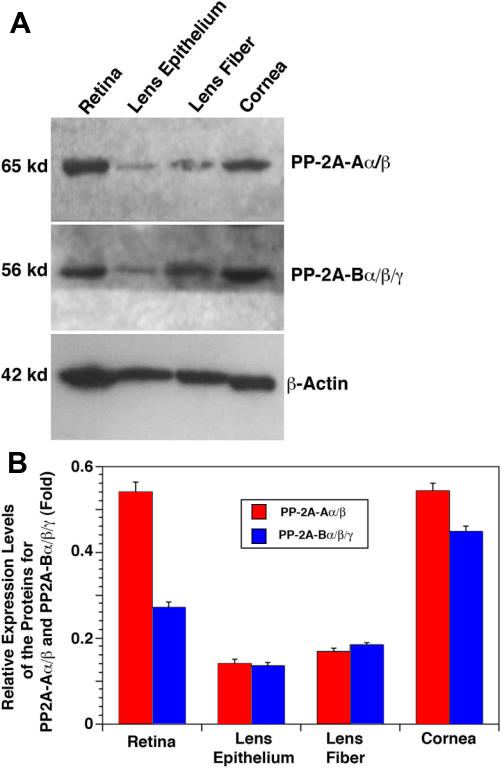
Figure 6.
Western blot analysis of the proteins for the regulatory subunits of PP2A-A and PP2A-B in the retina, lens epithelium, lens fiber, and cornea of the mouse eye. A: Fifty micrograms of total proteins extracted from different ocular tissues of the mouse eye were separated by 10% SDS–PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, and probed with an antibody recognizing both α and β isoforms of PP2A-A subunit (top panel) or an antibody recognizing all α, β and γ isoforms of PP2A-B subunit (middle panel) or an antibody recognizing β-actin (bottom panel) at a dilution of 1:500 (for PP-2A regulatory subunits) or 1:1000 (for β-actin) for 60 min. After three washes with TBS-T (10 mM Tris, pH 8.0; 150 mM NaCl; 0.05% Tween 20), the blots were incubated for 45 min with anti-mouse IgG (1:1000 dilution), which was linked to peroxidase. At the end of the incubation, the blots were washed twice with TBS-T followed by another two washes with TBS (10 mM Tris, pH 8.0; 150 mM NaCl) and finally visualized with the Amersham ECL kit. The molecular weight was determined according to the Bio-Rad protein standard. B: Quantitative results of the expression of the regulatory subunits of PP2A-A and PP2A-B in the retina, lens epithelium, lens fiber, and cornea of the mouse eye are shown in the chart. After exposure, the bands on each X-ray film were processed with the Automated Digitizing System from the Silver Scientific Corporation. The relative level of expression (fold) was calculated by dividing the averaged total pixel (from three experiments) for each band with the averaged total pixel from the corresponding β-actin band. Note that the two regulatory subunits, A and B, of PP-2A were predominantly expressed in the retina and cornea and at substantially reduced levels in the lens. In addition, expressions of the two regulatory subunits for PP-2A were slightly higher in lens fibers than in lens epithelial cells.