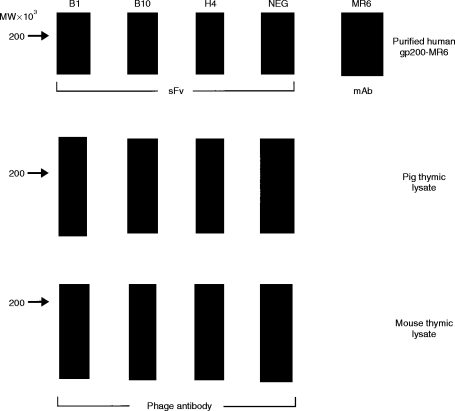
Figure 1.
Detection of either purified human gp200-MR6 or the homologous antigen in thymic lysates, from pig and mouse, using specific soluble sFv and phage antibody, respectively. Two micrograms of purified antigen, or thymic lysates were electrophoresed on 7·5% acrylamide gels, electroblotted onto nitrocellulose and probed with either sFv (purified antigen) or phage antibody (pig and mouse thymic lysates). Soluble sFv from the individual clones (B1, B10, H4) isolated after six rounds of panning on antigen, bound specifically to purified human gp200-MR6 in a similar manner to mAb MR6. In contrast, the control anti-NIP sFv (NEG)10 (encoded by DP-47 which belongs to the VH3 family) does not bind to gp200-MR6. This antibody was used in all subsequent experiments as a negative control antibody either as phage or as soluble sFv. Phage antibody specific for gp200-MR6 detected a band at around 200 000 MW on pig and mouse lysate suggesting that these antibodies recognize the homologous antigen in mouse and pig thymus.