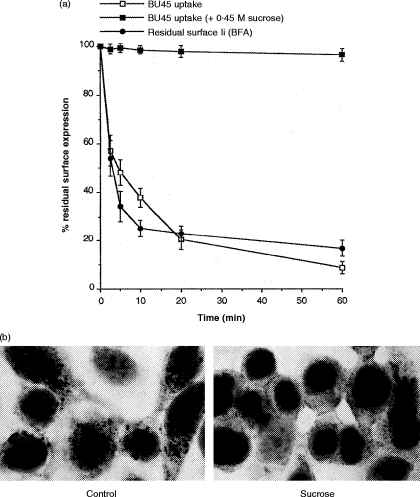
Figure 6.
(a) Rapid turnover of Ii on the surface of recombinant interferon-γ (rIFN-γ)-treated HT-29 cells. For internalization of surface-bound BU45, HT-29 cells pretreated for 72 hr with rIFN-γ were labelled with saturating amounts of BU45 on ice for 1 hr. After removing non-bound mAb, 50 μl of suspension containing 106 cells was added to 450 μl of medium, prewarmed to 37°, to allow endocytosis for different periods of time. Subsequently, cells were recooled by transfer to 4·5 ml of ice-cold medium and analysed for remaining surface-bound mAb by flow cytometry. Internalization of BU45 is depicted as the percentage of surface-bound mAb remaining after endocytosis at 37° relative to the total amount of mAb bound to cells that were kept on ice throughout. As a control, internalization of prebound BU45 was analysed under hyperosmotic conditions (0·45 m sucrose) known to inhibit coated pit-mediated endocytosis. The depletion of Ii from the plasma membrane at at steady state was measured after blocking transport of newly synthesized Ii by treatment with 1 μg/ml brefeldin A (BFA). Cells were preincubated with BFA for 15 min on ice followed by shifting the cells to 37° in the presence of BFA for different periods of time. The results are expressed as the percentage of Ii surface levels remaining after BFA treatment at 37° relative to the Ii level on cells not shifted to 37°. (b) HT-29 cells grown on slides were exposed to 100 U/ml IFN-γ for 24 hr. Control cells (Control) were incubated with saturating amounts of BU45 (50 μg/ml) in normal medium for 20 min at 37°. Alternatively, cells were preincubated for 10 min at 37° in hypertonic medium containing 0·45 m sucrose followed by further incubation for 20 min at 37° in the presence of 50 μg/ml BU45 diluted in the same sucrose-containing medium (0·45 m sucrose). Non-bound mAb was removed by rinsing in cold medium; subsequently, cells were acetone fixed and surface bound, and cytoplasmically located antibody was detected by immunocytochemical staining.