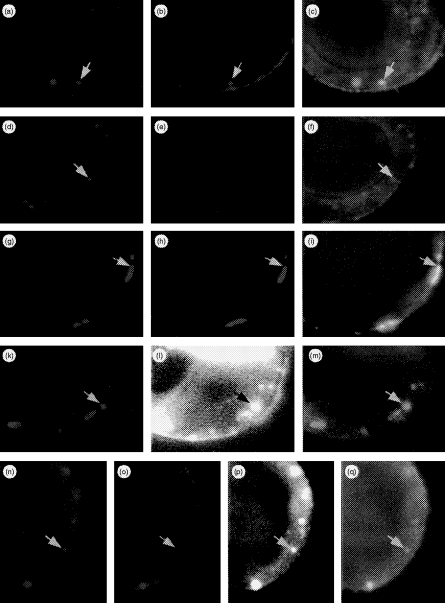
Figure 7.
Multicolour immunofluorescence microscopic analysis of antibody internalization. HT-29 cells grown on glass slides were stimulated for 36 hr with 500 U/ml recombinant interferon-γ (rIFN-γ). The antibodies were added simultaneously in various combinations. Absorption of antibodies was performed on ice for 30 min, after which the cells were washed and warmed at 37° to allow internalization for 10 min prior to acteone fixation. Bound and processed antibodies were then detected via isotype-specific goat antimouse antibodies carrying different fluorochromes. By combining filters, each spectral component of the image could be visualized individually or superimposed (rows 1–3). In an extension of these experiments, cells were additionally exposed to biotin-labelled bovine serum albumin (BSA; rows 4 and 5). Internalized BSA was detected via AMCA-conjugated streptavidin. Arrows mark identical areas of interest in different sets of filter combinations. First row: cells co-incubated with BU43 and L227 at 4° and then warmed to 37° show internalization of BU43 (a, red), L227 (b, green) in a co-localized manner (c: BU43/L227, yellow). Second row: cells co-incubated with BU43 and L243, and then treated as described above, show selective uptake of BU43 (d), while bound L243 antibodies remain at the cell surface (e) and therefore do not co-localize (f: BU43/L243). Third row: experimental setting as described for the first row except under hyperosmotic conditions. Antibody internalization of BU43 (g), L227 (h) is completely blocked resulting in their co-localization at the cell surface (i: BU43/L227). Fourth row: cells exposed to BSA at 37° for 10 min were acetone fixed to allow anti-Rab-5 antibody to penetrate the cells; Rab5 (k) and internalized BSA (l) are co-localized in early endosomes (m). Fifth row: in the presence of BSA, cells were exposed simultaneously to BU43 and L227. Co-internalized antibodies BU43 (n) and L227 (o) are targeted to the subcellular sites where BSA accumulates (p) resulting in co-localizion of BU43/L227/BSA (q). For enhancement of contrast, the AMCA blue in Fig. 1 and (p) has been changed to the pseudocolor white.