Table 4.
Correlation between CD44 expression, cytokine production, cytotoxicity and protection by hsp 65-specific T cell clones from BCG or DNA vaccinated mice
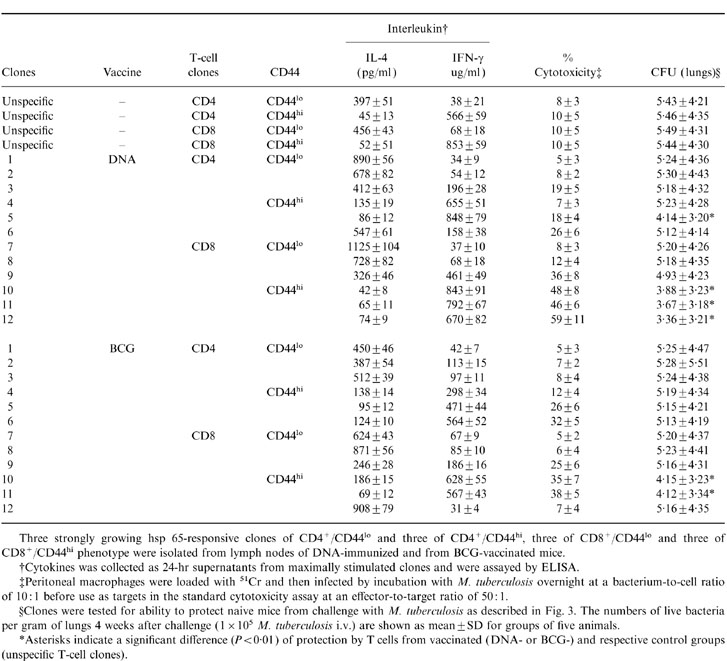
Three strongly growing hsp 65-responsive clones of CD4+/CD44lo and three of CD4+/CD44hi, three of CD8+/CD44lo and three of CD8+/CD44hi phenotype were isolated from lymph nodes of DNA-immunized and from BCG-vaccinated mice.
†Cytokines was collected as 24-hr supernatants from maximally stimulated clones and were assayed by ELISA.
‡Peritoneal macrophages were loaded with 51Cr and then infected by incubation with M. tuberculosis overnight at a bacterium-to-cell ratio of 10: 1 before use as targets in the standard cytotoxicity assay at an effector-to-target ratio of 50: 1.
§Clones were tested for ability to protect naive mice from challenge with M. tuberculosis as described in Fig. 3. The numbers of live bacteria per gram of lungs 4 weeks after challenge (1 × 105 M. tuberculosis i.v.) are shown as mean±SD for groups of five animals.
*Asterisks indicate a significant difference (P < 0·01) of protection by T cells from vaccinated (DNA-or BCG-)and respective control groups (unspecific T-cell clones).
