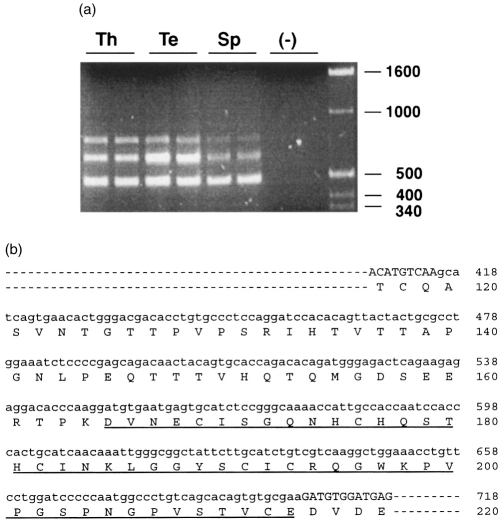
Figure 4.
Identification of alternatively spliced forms of mouse CD97. RT-PCR of the N-terminal region of mouse CD97 isoforms was performed with primers P5 and P9 (see the Materials and Methods) and with total RNAs from thymus (Th), testis (Te) and spleen (Sp). (a) Three fragments were amplified from all the tissues examined but not from the negative control reaction (−, no first-strand cDNA added). The smallest fragment corresponds to the three EGF domain-containing form of mouse CD97 shown in Fig. 2. Positions of molecular weight markers (in base pairs) are shown on the right. (b) Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the insertions in the two larger fragments shown in (a). Nucleotide sequence of the insertion is shown in lower case letters. The medium-sized fragment in (a) contains a 147-bp insertion which encodes a fourth EGF-like sequence repeat (underlined). The largest fragment in (a) contains a 282-bp insertion which encodes the same extra EGF-like sequence repeat plus a 45 amino acid sequence. In both fragments, the insertion occurs between EGF-like sequence repeat 2 and 3 of the cloned full-length mouse CD97 shown in Fig. 2. The numbering of nucleotide and amino acid sequences is the same as that shown in Fig. 2.