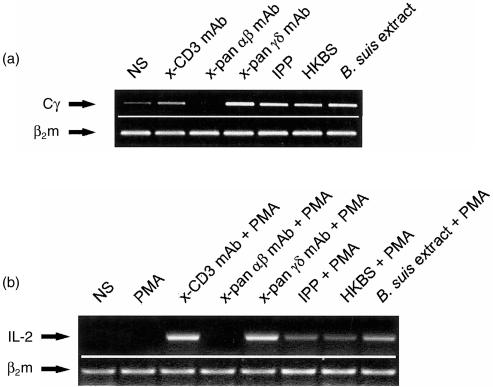
Figure 1.
Expansion of Vγ9Vδ2-bearing cells in response to heat-killed Brucella suis (HKBS) or B. suis extract. (a) Proliferation of γδ T cells from culture of peripheral blood mononuclear cells PBMC was determined by amplification of the Cγ transcript fragment using reverse transcription–polyerase chain reaction (RT–PCR) after 4 days of stimulation with HKBS or with B. suis crude extract. Anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody (mAb) was used as a general polyclonal T-cell mitogen, isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) or anti-pan γδ mAb as specific γδ T-cell activators, and anti-pan αβ mAb as a negative control. The intensity of the bands is clearly higher above basal level (non-stimulated [NS]) in HKBS and B. suis extract as well as in positive controls (anti-pan γδ mAb and IPP). (This is a representative experiment of at least five.) (b) Stimulation of DBS43 was performed in the presence of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) as a costimulatory signalling molecule. Cell activation was estimated by amplification of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) mRNA fragment using RT–PCR after 6 hr of stimulation. PMA alone, inefficient for stimulating Jurkat cells, was used as a negative control. Other positive and negative controls were similar to those used in Figure 1a). HKBS and B. suis extract, as well as positive controls (anti-CD3, anti-pan γδ mAb and IPP), appear to induce IL-2 gene transcription in these Vγ9Vδ2-transfected Jurkat cells. (This is a representative experiment out of three.)