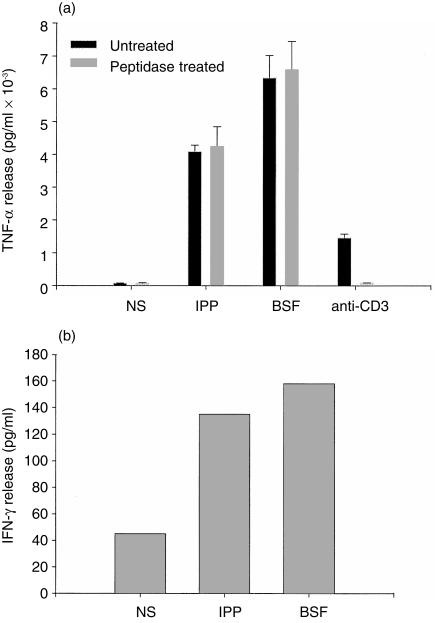
Figure 3.
Analysis of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) production by isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) or Brucella suis low-molecular-weight fraction (BSF)-activated γδ T cells. (a) Human γδ T cells, previously treated or untreated with proteinase K, were stimulated or unstimulated with IPP, BSF or anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody (mAb). After 24 hr, the supernatant was tested for its cytotoxic activity against L929 fibroblasts, and TNF-α level was estimated by comparison to a reference curve established using serial dilutions of human recombinant TNF-α (rTNF-α). Anti-CD3 mAb was used as a proteic mitogenic control to test the efficacy of proteinase K treatment. (This is a representative experiment out of three.) (b) Human γδ T cells were stimulated for 24 hr with IPP or BSF, and the concentration of IFN-γ (in pg/ml) was determined in the resulting culture supernatants by using a commercial IFN-γ enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit. (This experiment was repeated twice.)