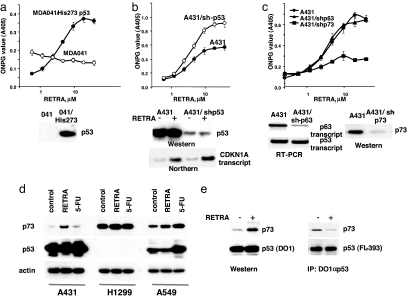
Fig. 3.
Transcriptional activity of RETRA requires expression of mutant p53 and depends on induction of p73. (a) (Upper) RETRA acquires dose-dependent activation of lacZ reporter in p53-null human fibroblasts MDA041 after introduction of recombinant for expression of mutant p53 Arg273His (treatment with RETRA for 14 h, ONPG reaction). (Lower) Level of p53 protein determined by Western blot analysis with monoclonal antibodies DO1. (b) (Upper) Partial inhibition of mutant p53 in A431 cells by expression of shRNA activates the induction of p53-dependent reporter in response to RETRA (ONPG reaction). (Lower) Levels of mutant p53 protein determined by Western blot analysis with DO1 antibodies and levels of CDKN1A (p21) transcripts determined by Northern blot hybridization in the control and p53-shRNA-expressing cells, untreated, or treated with 1.5 mg/ml RETRA. (c) (Upper) Partial inhibition of p63 by shRNA does not affect response of A431/LC5 reporter cells to RETRA; partial inhibition of p73 by shRNA abrogates the induction of A431/LC5 reporter in response to treatment with RETRA. (Lower) levels of transcripts from the p63 gene (RT-PCR) and levels of p73 protein (Western blot analysis with TA/p73-specific antibodies). (d) Changes in the levels of p73 protein in A431, H1299, and A549 cell lines after treatment with 2 μg/ml RETRA or 5 μg/ml 5-fluorouracil for 20 h. Western blot analysis with antibodies specific to TA/p73. The samples were normalized for expression of β-actin and also probed for expression of p53 with monoclonal antibodies DO1. (e) Changes in proportion of mut-p53-bound p73 after treatment of A431 cells with 2 μg/ml RETRA for 20 h. (Left) Western blot analysis of 100 μg per lane of total lysates probed with rabbit TA/p73-specific Ab and α-p53 monoclonal Ab DO-1. (Right) IP of 2 mg of lysates probed with rabbit TA/p74 Ab or with rabbit p53 Ab FL-393.