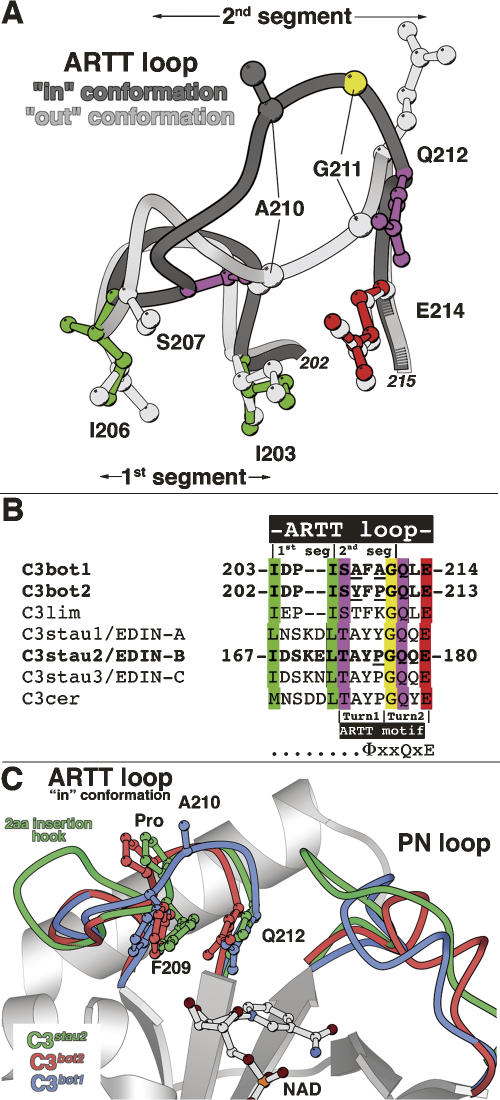
Figure 5.
The ARTT loop in C3-like exoenzymes. (A) The two structural segments of the ARTT loop. Superposition of the two distinct conformations of the ARTT loop (dark and light gray) are shown with critical residues for understanding its structural properties. The first segment encompasses two conserved anchor hydrophobic residues (I203 and I206 in green for the “in” conformation). The second segment encompasses two hinge residues, Ser207 and Gln212 (in purple for the “in” conformation), which allow the ARTT loop conformational change. Gly211 (in yellow for the “in” conformation) from this second segment makes the most important deviation between both conformations. Note that the catalytic glutamate is highlighted in red (for the “in” conformation). Equivalent residues from the “out” conformation are shown in light gray for clarity. (B) Sequence alignment of the C3-like exoenzymes. The color code is conserved with the “in” conformation shown in Figure 5A. In bold are the C3 isoforms for which the structure is known. (Underline) Differences in sequence among C3bot1, C3bot2, and C3stau2 mentioned in the text. Note that the position of the two turns of the ARTT motif are indicated (Han and Tainer 2002). (C) Superimposition of the ARTT loop “in” conformation of the C3bot1 (C3wt-NAD; molA), C3bot2, and C3stau2 structure.