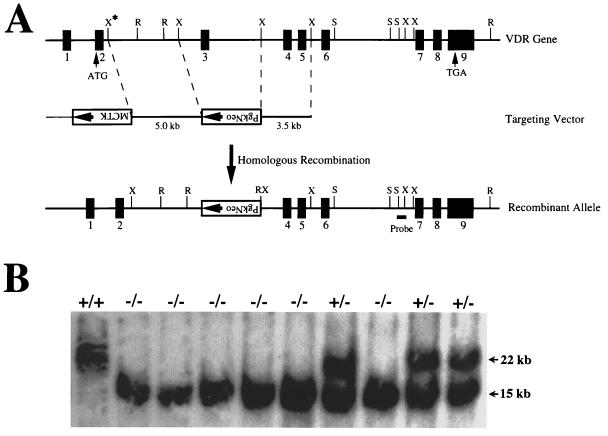
Figure 1.
Targeting strategy for VDR ablation. (A) Construction of targeting vector for VDR ablation. A schematic representation of the VDR gene is shown, based on the structure of the human gene and characterization of the sequences from exon 3 to exon 9 of the mouse gene. The exons are numbered and indicated by solid boxes. A partial restriction map is shown for the following enzymes: R, EcoRI; X, XbaI; S, SacI. The XbaI site indicated by the asterisk was derived from the phage arm. A 5-kb XbaI fragment 5′ to exon 3 and a 3.5-kb XbaI fragment 3′ to exon 3 of the mouse VDR gene were used as the targeting sequences. The SacI-XbaI fragment used as a probe for identifying homologous recombinants is indicated. (B) Genomic Southern analysis of tail DNA derived from offspring of heterozygous matings. The DNA was digested with EcoRI and hybridized with the external probe as indicated in A. The wild-type allele generates a 22-kb fragment, and the mutant allele resulting from homologous recombination produces a 15-kb fragment. Wild-type mice are indicated by +/+; heterozygous, by +/−; and homozygous receptor ablated mice, by −/−.