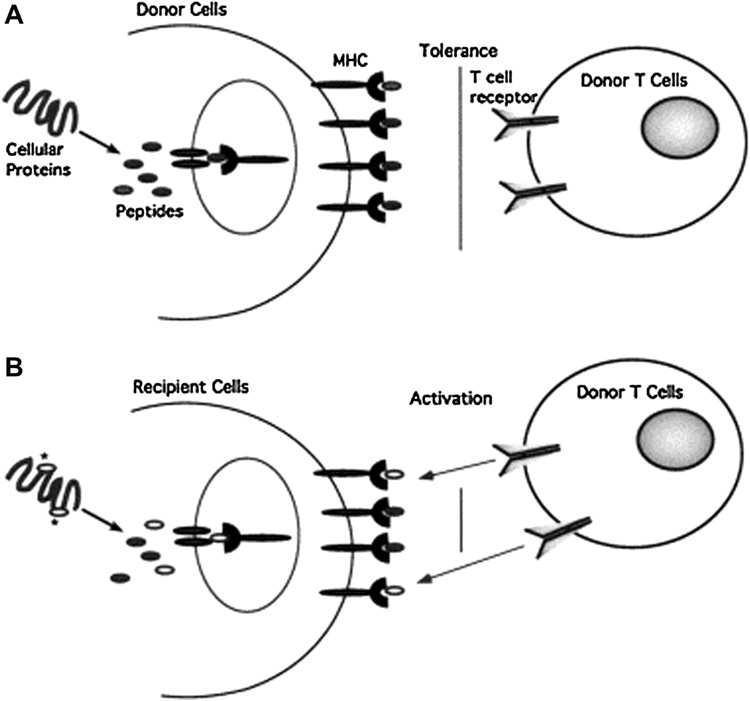
Figure 1.
Minor histocompatibility antigens represent distinct MHC-bound peptides displayed by MHC identical recipient cells. (A) Peptides derived from cellular proteins are displayed on the surface of cells complexed to MHC molecules and autologous T cells are tolerant to these self-peptides. (B) Due to polymorphisms in the genome, cellular proteins expressed by recipient cells may contain amino acid substitutions (depicted by the asterisks) compared with the homologous proteins in donor cells. After processing, these sequences may provide unique peptides that bind to MHC molecules and are displayed at the cell surface. T cells of the donor will recognize the unique peptides on recipient cells as foreign. Reproduced with permission from Riddell SR, Berger C, Murata M, et al. The graft versus leukemia response after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Rev. 2003 Sep;17(3):153-62.