Figure 8.
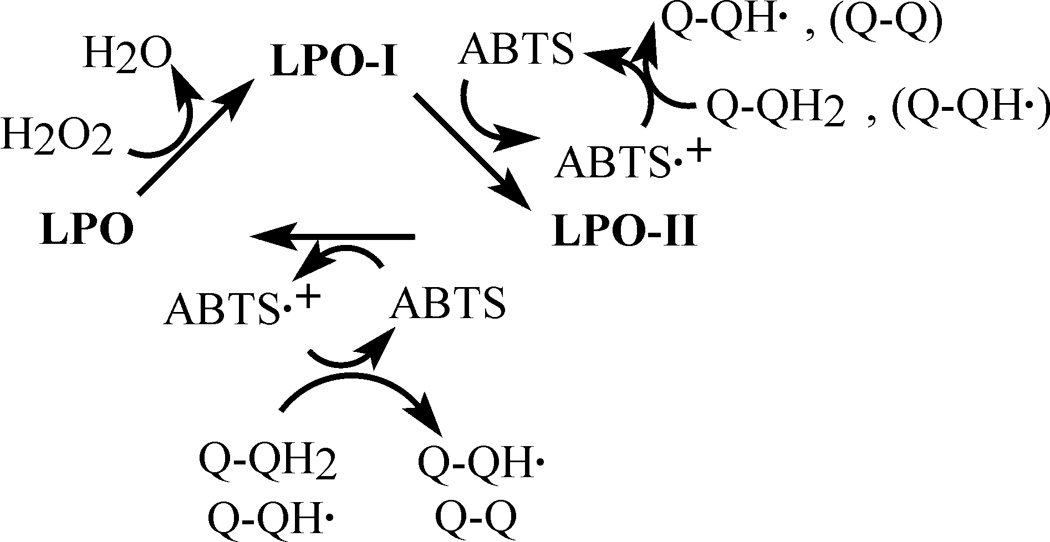
Proposed mechanism of the inhibitory action of DOX on oxidation of ABTS by LPO/H2O2. The inhibition is due to reduction of ABTS•+ by the drugs’ hydroquinone moiety forming a DOX-derived semiquinone, which also reacts with ABTS•+. LPO, LPO-I, LPO-II represent the ferric enzyme, and LPO compounds I and II, respectively. Q-QH2, Q-QH• and Q-Q designate redox-active groups of intact doxorubicin, a doxorubicin free radical (quinone-semiquinone form), and the di-quinone form of DOX, respectively.
