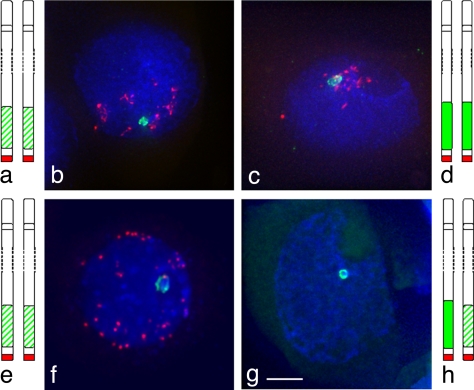
Fig. 2.
Heterochromatin colocalization and association at meiosis. Subtelomeric heterochromatin, labeled in green, uses the pSc250 rye sequence as a probe and telomeres, in red, use a PCR product derived from primers (5′-TTTAGGG-3′)5 and (5′-CCCTAAA-3′)5 as the probe. In the lines Petkus/Petkus (a and e) and King II/King II (d), with identical heterochromatin, the chromosomes can colocalize before the telomere bouquet (b and c) and can associate as a fork after telomere bouquet (f). In the line Petkus/King II (g and h), with similarly sized heterochromatin, the segments associate as a ring structure. (Scale bar: ≈10 μm.)