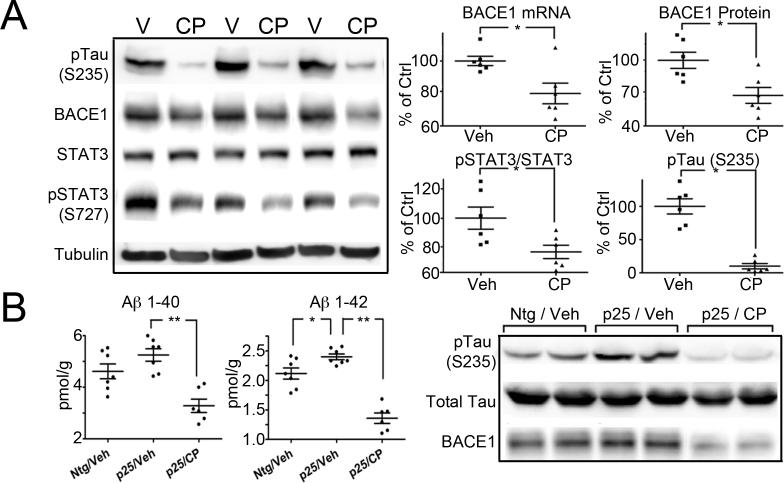
Figure 5. Inhibition of cdk5 activity reduces Aβ production and BACE1 levels in vivo.
Panel A: Representative immunoblots of pTau(S235), BACE1, STAT3, pSTAT3(S727) and tubulin in brain lysate from vehicle (V) and CP-681301 (CP) treated Ntg mice. BACE1 mRNA and protein levels, together with pSTAT3(S727)/STAT3 and pTauS235 are shown as scatterplots. N=6 in each group. There was a significant difference (p<0.05) between vehicle and CP-681301 treated mice for the proteins of interest. Panel B: Three groups of young (5 day old) mice were analyzed for Aβ and BACE1 levels: Ntg mice treated with vehicle (Veh; n=7), p25 mice treated with vehicle (p25/veh; n=7) and p25 mice treated with CP-681301 (p25/CP; n=6). Aβ40 and 42 levels were elevated in p25 mice relative to Ntg mice. Administration of CP-681301 to p25 mice significantly reduced both peptides (p<0.01). BACE1 was elevated in p25 mice relative to Ntg mice but was significantly reduced by CP-681301. The relative activity of cdk5 was shown by phosphorylation of Tau at the S235 site. Total tau levels indicated that equivalent levels of protein were loaded. All results were analyzed with Student's t-test, * p<0.05 ** p<0.01.