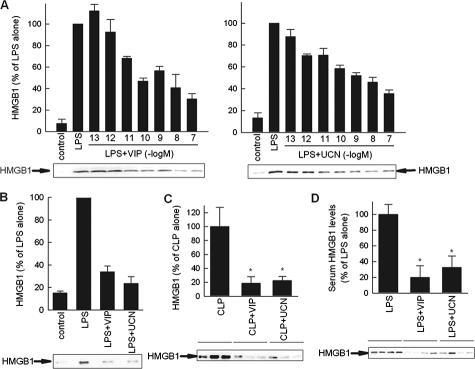
Figure 4.
VIP and UCN reduce HMGB1 secretion by targeting macrophages. A and B: VIP and UCN inhibit the secretion of HMGB1 in endotoxin-activated RAW 264.7 (A) or peritoneal (B) macrophages were cultured with medium (control) or stimulated with LPS (1 μg/ml) and different concentrations of VIP or UCN (10−7 M for peritoneal macrophages) for 24 hours. HMGB1 content in culture supernatants was assayed by Western blotting and expressed as densitometric units relative to the LPS-treated condition on the same blot (HMGB1-specific band is indicated by an arrow). Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 to 5). C: VIP and UCN deactivate peritoneal macrophages during sepsis. Mice were subjected to CLP and treated i.p. with VIP or UCN (1 nmol/mouse) 12 hours later. Peritoneal lavage was obtained 18 hours after sepsis induction. Peritoneal macrophages were isolated and cultured with medium at 106 cells/ml for 36 hours. The concentration of HMGB1 in the culture supernatants was determined by Western blotting and expressed as band densities relative to control samples (CLP alone) on the same blot. Data are mean ± SEM n = 8 per group *P < 0.001 versus CLP alone (Mann-Whitney test). D: VIP and UCN down-regulate LPS-induced HMGB1 secretion in vivo. Endotoxemia was induced by i.p. injection of LPS (100 μg/mouse). Mice were treated 30 minutes later with medium (controls) or with VIP (1 nmol) or UCN (1 nmol). Serum was collected 24 hours after endotoxin administration and circulating HMGB1 levels were determined by Western blot (HMGB1-specific band is indicated by an arrow), and expressed as band densities relative to control samples (LPS alone) on the same blot. Data are mean ± SEM *P < 0.05 versus LPS alone (Mann-Whitney test). n = 7 to 10 mice per group.