Table 1. Crystallographic data, refinement statistics and analysis of the quality of MtSK structures.
Values in parentheses are for the outermost shell.
| MtSK–ADP–shikimate | MtSK–MgADP | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystallographic data | ||
| Unit-cell parameters | ||
| a (Å) | 63.3 | 60.2 |
| b (Å) | 63.3 | 62.2 |
| c (Å) | 91.6 | 170.6 |
| Space group | P3221 | P212121 |
| No. of measurements | 76792 | 97059 |
| No. of independent reflections | 16017 | 17057 |
| Completeness (%) | 96.9 (91.5) | 99.4 (96.9) |
| Rsym† (%) | 8.9 (58.8) | 12.1 (58.0) |
| Redundancy | 4.8 | 5.7 |
| Refinement statistics | ||
| Resolution range (Å) | 35.16–1.93 | 57.17–2.80 |
| Reflections used for refinement | 15130 | 15670 |
| Final R factor‡ (¨%) | 20.2 | 18.3 |
| Final Rfree§ (%) | 27.0 | 28.0 |
| Correlation coefficient (%) | 95.2 | 94.3 |
| B values (Å2) | ||
| Main chain | 31 | 33 |
| Side chain | 34 | 36 |
| ADP | 21 | 27 |
| Shikimate | 32 | — |
| Waters | 39 | 30 |
| Quality of structure | ||
| Three-dimensional profile¶ | S = 88.07, IS = 74.95, S/IS = 1.18IS | S = 343.59, IS = 294.34, S/IS = 1.17IS |
| Ramachandran plot | ||
| Favoured | 95.6 | 84.8 |
| Additionally allowed | 2.9 | 13.3 |
| Generously allowed | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Disallowed | 0.7 | 1.1 |
R
sym = 100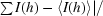
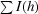 , where I (h) is the observed intensity and 〈I(h)〉 is the mean intensity of reflection h over all measurements of I(h).
, where I (h) is the observed intensity and 〈I(h)〉 is the mean intensity of reflection h over all measurements of I(h).
R factor = 100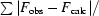
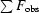 , the sums being taken over all reflections with F/σ(F) > 2σ(F).
, the sums being taken over all reflections with F/σ(F) > 2σ(F).
R free is the R factor for 10% of the data that were not included during crystallographic refinement.
The ideal score measures the compatibility of a protein model with its sequence, using a 3D profile. Each residue position in the 3D model is characterized by its environment and is represented by a row of 20 numbers in the profile. These numbers are the statistical preferences (called 3D-1D scores) of each of the 20 amino acids for this environment. Environments of residues are defined by three parameters: the area of the residue that is buried; the fraction of side chain area that is covered by polar atoms (O and N) and the local secondary structure. The 3D profile score S for the compatibility of the sequence with the model is the sum, over all residue positions, of the 3D-1D scores for the amino-acid sequence of the protein. For 3D protein models known to be correct, the 3D profile score S for the amino-acid sequence of the model is high, by contrast, the profile score S for the compatibility of a wrong 3D protein model with its sequence is often low. When this method is used to verify a structure, the raw compatibility score alone is difficult to interpret. In this case it is necessary to compare the score to those obtained using structures known to be correct, we use the Ideal Score (IS), that is calculated from the length of the protein. The IS is determined by 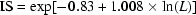 . Where L is the length of the sequence. Severely misfolded structures typically have scores less than 0.45 IS. A score near or above IS indicates a reliable structure.
. Where L is the length of the sequence. Severely misfolded structures typically have scores less than 0.45 IS. A score near or above IS indicates a reliable structure.
