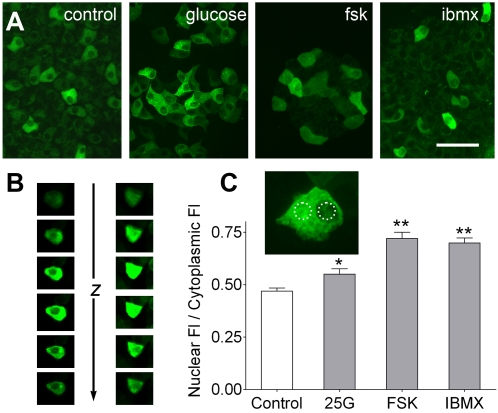
Figure 7. Elevation of cAMP causes PKA catalytic subunit translocation to the nucleus in β-cells.
A. Islets from induced Ins2-rtTA/pBI-cAMP mice were incubated for 30 min in control media or with added glucose (25 mM), forskolin (10 µM) or IBMX (100 µM). Nuclear C-YFP fluorescence is visible after prolonged elevation of cAMP (especially with fsk) in contrast to cytoplasmic localization in control islets. Scale bar, 20 µm. B. Z-stacks of confocal images to illustrate cytoplasmic C-YFP (i.e. with dark nucleus, left) and nuclear translocated (i.e. with bright nucleus, right) following IBMX for 30 min. C. Fluorescence intensity was quantified in Regions Of Interest (dotted circles in inset) over the nucleus and cytoplasm of cells treated as in A. The ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic fluorescence was significantly higher relative to control when cAMP levels were elevated (* p≤0.05; ** p≤0.01; Dunnett's multiple comparisons test; n = 24–47 cells in 3 experiments for each treatment).