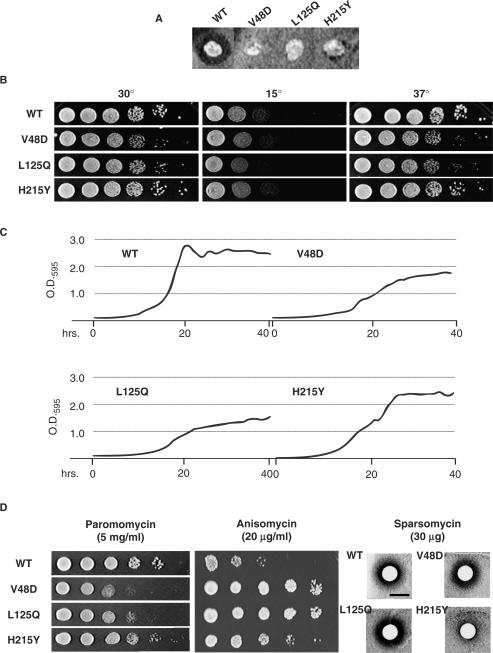
Figure 2.
The L2 mutants promote numerous phenotypic defects. (A) ‘Killer’ virus phenotypes. The Killer+ phenotype is scored by the presence of a halo of growth inhibition around wild-type colony. Lack of the halo around colonies expressing the V48D, L125Q and H215Y L2 mutants indicates the Killer− phenotype. (B) Ten-fold dilutions of indicated cells were spotted onto rich medium and incubated at the indicated temperatures. (C) Yeast cell growth was monitored for 40 h at 30°C with a Synergy HT micro-plate reader and growth curves were generated from four independent readings utilizing the KC4 software package. (D) Drug-sensitivity phenotypes. To monitor changes in sensitivity to paromomycin and anisomycin, 10-fold serial dilutions of each strain were spotted onto rich medium containing these drugs at the indicated concentrations. Sensitivity to sparsomycin was monitored using 6-mm Whatman filter discs saturated with 30 µg of sparsomycin placed onto the center of plates seeded with OD595 = 0.2 of yeast cells expressing the indicated L2 mutants.