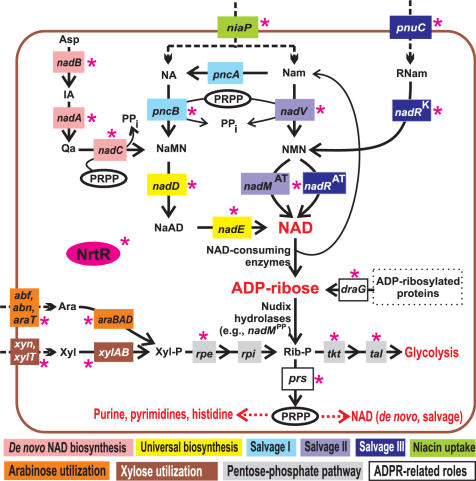
Figure 1.
Overview of NAD biosynthesis and salvage pathways and a link with other metabolic pathways via ADP-ribose. NrtR-controlled steps are indicated by a red asterisk. Metabolic enzymes and uptake transporters are shown by solid and dashed lines, respectively and colored by a metabolic pathway. De novo NAD biosynthesis pathway utilizes L-aspartate oxydase (the product of nadB gene), quinolinate synthase (nadA) and quinolinate phosphoribosyltransferase (nadC). Universal NaMN to NAD pathway utilizes nicotinate mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (nadD), and NAD synthetase (nadE). In Nam salvage pathways, NaMN is synthesized from NA and Nam precursors that are taken up by niacin transporter (niaP). Salvage I pathway involves nicotinamide deaminase (pncA), and nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase (pncB). Salvage II pathway uses nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (nadV), and nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (nadMAT) (31,41). In the third salvage pathway, NAD is synthesized from the exogenous RNam precursor delivered by the RNam transporter (pnuC) via consecutive reactions catalyzed by two separate domains of NadR, nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (nadRAT), and nicotinamide riboside kinase (nadRK)(47,48). Endogenous Nam and ADP-ribose are generated by enzymes hydrolyzing the N-glycosidic bond of NAD. Enzymes linked to NAD metabolism via ADP-ribose are ribose phosphate pyrophosphokinase (prs); ribose phosphate isomerase (rpi), ribulose phosphate epimerase (rpe), transketolase (tkt), transaldolase (tal), as well as xylose (xylAB), and arabinose (araBAD) utilization enzymes. Asp, aspartate; Trp, tryptophan; IA, iminoaspartate; Qa, quinolinic acid; NaMN, nicotinate mononucleotide; NaAD, nicotinate adenine dinucleotide; NA, nicotinic acid; Nam, nicotinamide; RNam, ribosyl nicotinamide; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; ADPR, ADP-ribose; PRPP, phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate; Rib-P, ribose-5-phosphate; Xyl-P, xylulose-5-phosphate; Ara, l-arabinose; Xyl, d-xylose.