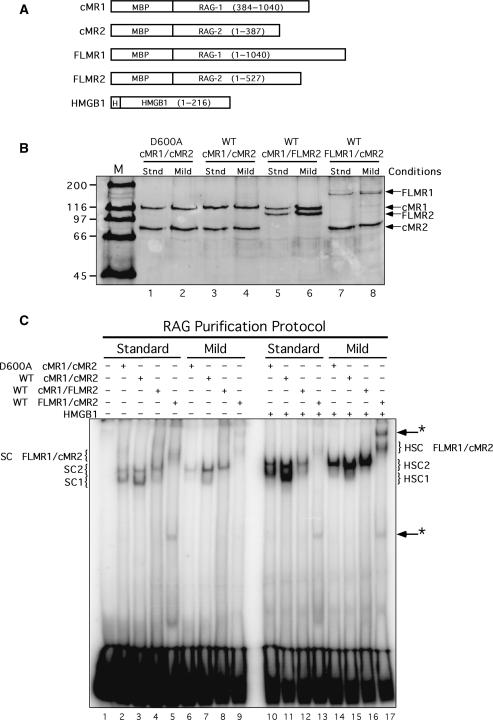
Figure 1.
Core and full-length RAG proteins purified using different conditions exhibit distinct DNA binding properties. (A) Schematic diagrams of RAG1, RAG2 and HMGB1 fusion proteins used in this study. MBP and polyhistidine (H) sequences are also indicated. (B) Purified proteins analyzed by SDS–PAGE. WT or catalytically inactive (D600A) RAG1 and RAG2 fusion proteins shown in (A) were co-expressed in HEK 293 cells in the indicated combinations and purified by amylose affinity chromatography using standard (stnd) or mild buffers (see ‘Materials and Methods’ section). Proteins were fractionated by SDS–PAGE in parallel with protein standards (M) and detected by staining the gel with SYPRO orange. (C) EMSA of RAG protein preparations. Radiolabeled intact 12-RSS substrate was incubated with cMR1/cMR2 (WT or D600A), cMR1/FLMR2 or FLMR1/cMR2 purified using standard or mild conditions in binding reactions lacking or containing HMGB1 as indicated above the gel. Protein–DNA complexes were fractionated by EMSA. The positions of SC1, HSC1, SC2, HSC2 species (described in the text) are indicated at left and right. Novel protein–DNA complexes are denoted by arrows with an asterisk at right.