Figure 6.
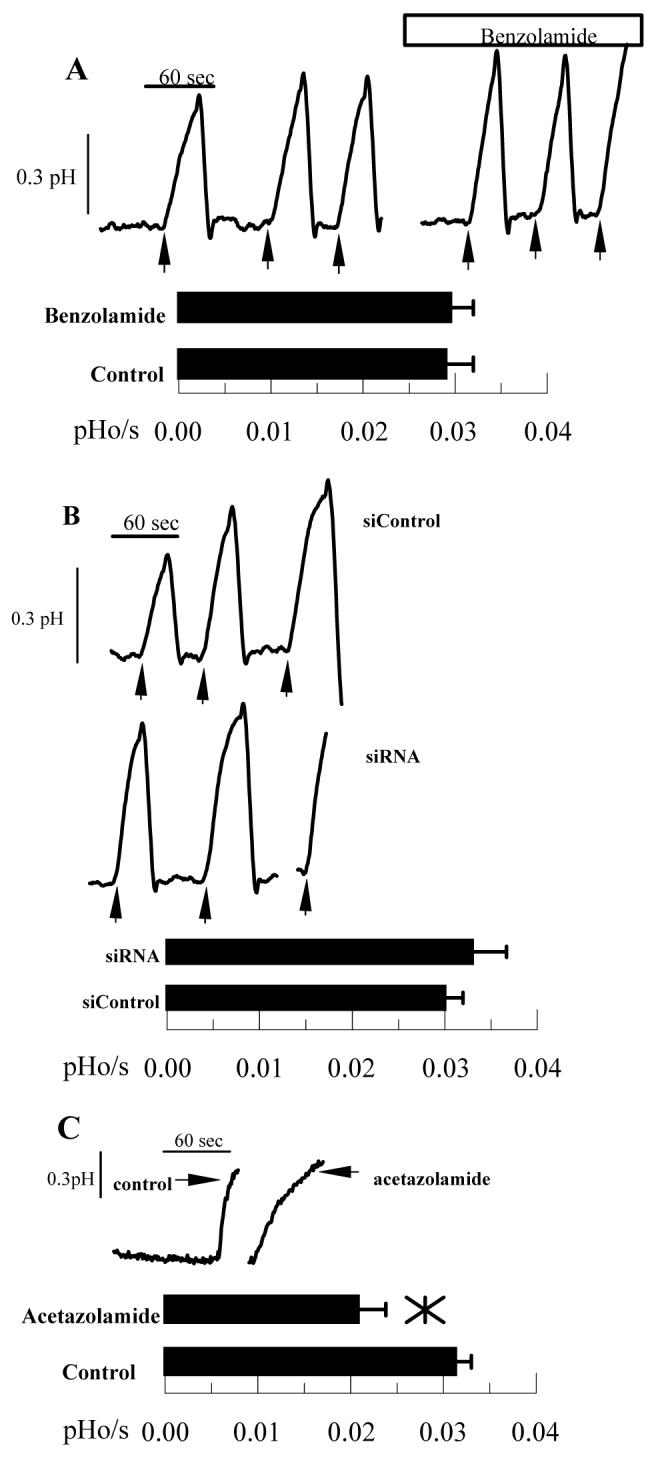
Effect of Benzolamide and CAIV siRNA on basolateral to apical HCO3- Flux. Endothelial cells were perfused with bicarbonate-rich ringer in a two-sided chamber. The apical ringer was then changed to LB ringer (pH 6.5) containing 1 μM BCECF free acid to measure apical ringer pH. Arrows indicate when apical perfusion was stopped and apical outflow clamped. A. This was performed three times in the absence and then in the presence of 10 μM benzolamide on the apical side. Bar graph shows mean rates and SD (n=12 anodiscs). B. Representative comparisons of siControl and CAIV treated cells. Bar graph shows mean rates and SD (n=10 anodiscs). C. Positive control; representative traces showing decreased HCO3- flux with 50 μM acetazolamide (n=4) on both basolateral and apical sides.
