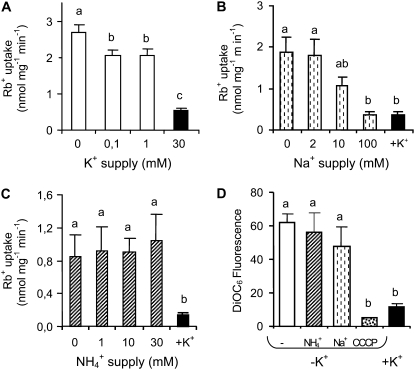
Figure 6.
High sodium, but not high ammonium, concentrations interfere with the increased contribution of HvHAK1 following K+ starvation in yeast cells. HvHAK1-expressing yeast cells were grown overnight at 30 mm KCl and then exposed for 210 min to different external concentrations of alkali cations. A, Rb+ uptake from a 100 μm Rb+ solution after cells were exposed to different external K+ concentrations (n = 4). B and C, Rb+ uptake for cells exposed for 210 min to the absence of K+ in the presence of different Na+ concentrations (n = 3) or NH4+ concentrations (n = 5), respectively. D, Accumulation of the fluorescent dye DiOC6 measured in yeast cells grown for 210 min in the absence of K+ with or without 30 mm NH4+, 100 mm Na+, or 20 μm carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) uncoupler as well as in the presence of 30 mm KCl (n = 5). Error bars represent se. Different letters indicate significantly different values (P < 0.05 for A to C, P < 0.005 for D).