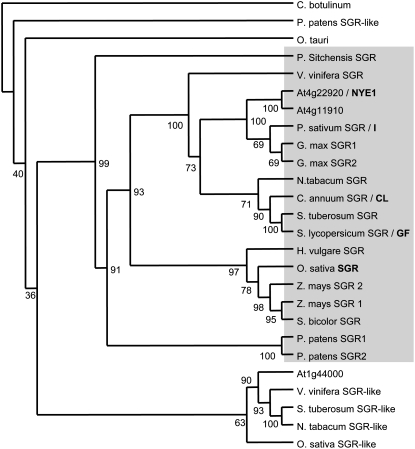
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis of the SGR family. Protein alignments based using N terminus deleted amino acid sequences were performed using ClustalX. Phylogenetic relationships between the proteins were analyzed using the PHYLIP 3.67 suite of programs (http://evolution.genetics.washington.edu/phylip.html). The maximum parsimony, distance matrix, and likelihood methods of the Protpars and Seqboot programs were utilized to estimate phylogenies. A nonrooted tree phylogenetic tree was generated using Consense and the Treeview package using the Clostridium botulinum protein as the outgroup. The single most parsimonious tree obtained in a heuristic search following 100 random sequence addition replicates is shown. Bootstrap percentage supports are indicated at the branches of the tree. Sequence identifiers and accession numbers are described in “Materials and Methods.” Proteins shown in bold indicate where a mutant phenotype has been described.