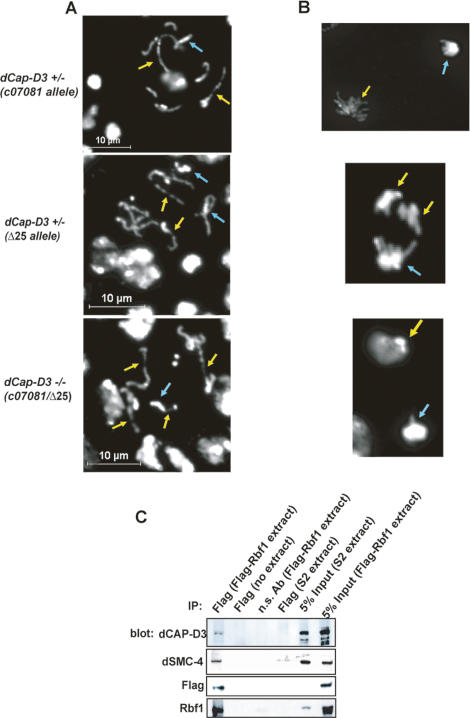
Figure 3.
dCAP-D3 physically interacts with RBF1 and is necessary for uniform chromatin condensation. (A) Prophase/prometaphase spreads of neuroblast squashes from Drosophila third instar larvae heterozygous or null for dCap-D3 show chromatin hypocondensation phenotypes that are very similar to those seen in rbf1 mutants (Fig. 1). Yellow arrows mark regions of chromosomes that are hypocondensed. Blue arrows mark regions of chromosomes that are more condensed. (B) Anaphase spreads of neuroblast squashes from Drosophila larvae of the genotypes described in A. Yellow arrows indicate the group of chromosomes that are hypocondensed compared with the other group of chromosomes in the anaphase pair. (C) Condensin II subunits coimmunprecipitate with RBF1. Immunoblotting was performed using antibodies to Condensin II subunits dCAP-D3 and dSMC4. Extracts of SL2 cells, or SL2 cells stably expressing Flag-RBF1, were immunopreciptated with antibody to Flag-RBF1 or a nonspecific control antibody. Note that dCAP-D3 and dSMC4 coimmunopreciptated with Flag-RBF1; no signal was seen using either the control antibody or control lysates.