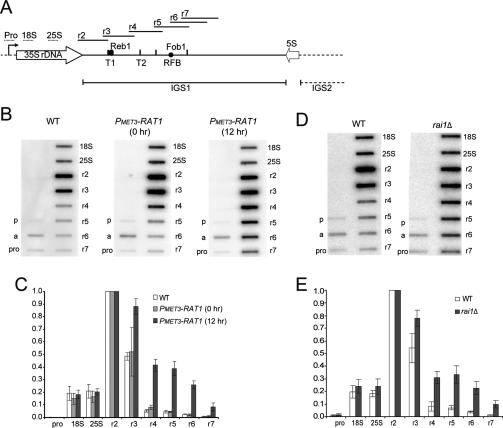
Figure 5.
TRO shows read-through of the major Pol I terminator in strains lacking Rat1 or Rai1. (A) rDNA schematic showing the positions of M13 phage TRO probes depicted as horizontal bars above the rDNA sequence (see also Prescott et al. 2004). Labels are as in Figure 2A. (B,C) TRO analysis of wild-type and PMET3-RAT1 strains. (B) Representative TRO profiles are shown for the isogenic wild type grown in the presence of methionine (5 mM) and for PMET3-RAT1 cells grown in the absence (0 h) or presence of methionine for 12 h to allow depletion of Rat1. (pro) Promoter; (a) ACT1-positive control. (p) negative control. (C) Quantifications of TRO signals were corrected for background hybridization (probe p) and uracil content, and normalized to probe r2, which was arbitrarily set to 1. The mean of three independent experiments is shown with standard deviation. Lower signals over the regions encoding the 18S and 25S rRNAs were observed previously (see the Supplemental Material in Jones et al. 2007) and may reflect quenching of the signals by the highly abundant rRNAs. (D–E) TRO analysis of wild-type and rai1Δ strains (BY4741 background) grown in minimal medium at 30°C. D as B. E as C. Similar data (not shown) were observed with W303-1a background.