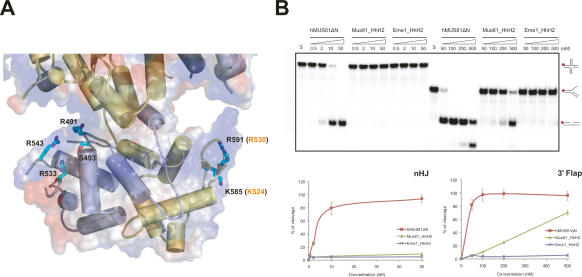
Figure 5.
Analysis between HhH2 domains of cMUS81 and DNA substrates. (A) Structure of the two HhH2 domains of cMUS81. Secondary structures of zMus81ΔN are colored in yellow, and hEme1ΔN are light blue. The side chains of zMus81ΔN and hEme1ΔN that are mutated to glutamate in our analysis are colored in cyan. Equivalent residue numbers of hMus81ΔN are shown in orange. (B, top) Nuclease activities of wild-type and HhH2 mutant proteins of hMus81ΔN and hEme1ΔN. For Mus81_HhH2, Lys524 and Arg530 of hMus81ΔN were replaced with Glu simultaneously. For Eme1_HhH2, Arg491, Ser493, Arg533, and Arg543 of hEme1ΔN were replaced with Glu simultaneously. The nHJ and 3′ flap DNA substrates reacted with increasing amount of wild-type or HhH2 domain mutant hMUS81ΔN. Numbers at the top of the lanes indicate protein concentrations (nanomolar). DNA structures with a 32P-labeled 5′ end (red circle) are shown in the right column. (Bottom) The total amount of cleavage products was quantified by PhosphorImager analysis and expressed as a percentage of total radiolabel.