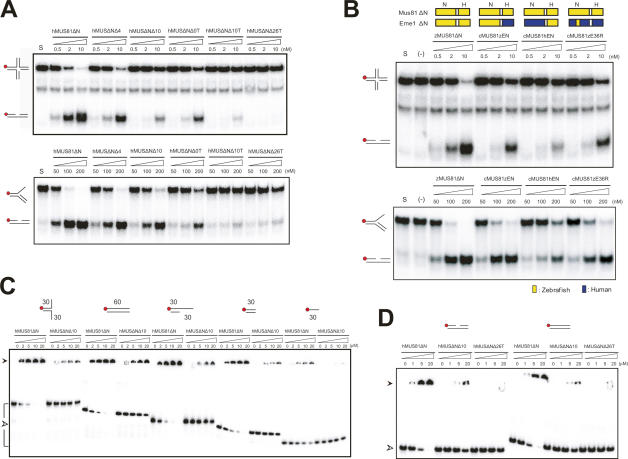
Figure 6.
Roles of the 36R intradomain linker of Eme1. (A) Nuclease activity of wild-type hMUS81ΔN and the 36R linker deletion mutant proteins. The 60mer nHJ and 3′ flap DNA substrates (62.5 nM) were incubated for 60 min at 37°C with increasing amounts (nanomolar) of wild-type or mutant hMUS81ΔN. The top panel shows protein constructs with the numbers of deleted residues and cleavage of a 36R linker. For instance, hMUSΔNΔ4 represents a mutant in which four residues of the 36 linker are deleted, and hMUSΔNΔ10T (ternary complex) represents a mutant in which the 36 linker is cleaved into two parts and 10 residues are deleted. DNA structures with a 32P-labeled 5′ end (red circle) are shown at the left side. Reaction products were analyzed by 10% native polyacrylamide gel. (B) DNA cleavage assay of chimeric Eme1 mutants. A schematic diagram shows the construct of each mutant. (Top) Components from zebrafish Mus81 (or Eme1) and human Mus81 (or Eme1) are colored in yellow and blue, respectively. cMUS81zEN indicates an Eme1 construct with a zebrafish nuclease domain (zEN) with a human HhH domain, and cMUS81hEN represents an Eme1 construct with a human nuclease domain (hEN) and a zebrafish HhH domain. cMUS81(zE36R) indicates hEme1 mutant in which 36R linker is substituted with an equivalent region of zEme1. (C) Binding assays between 36R linker deletion mutant proteins and various DNA substrates. Substrate structures used for analysis are shown on the top. Numbers indicate the lengths of nucleotides. Red circles show the 32P-labeled 5′ DNA end. Reaction mixtures were analyzed on 8% native gel. (D) Binding assays between 36R linker deletion mutant proteins and a duplex DNA or a nicked DNA. Substrate structures used for analysis are shown at the top. Red circles show the 32P-labeled 5′ DNA end. Reaction mixtures were analyzed on 8% native gel.