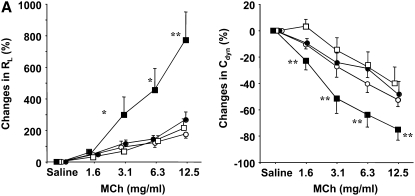
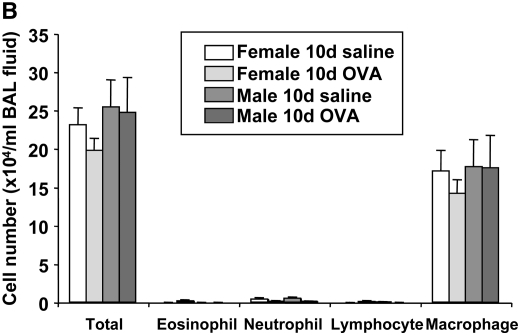
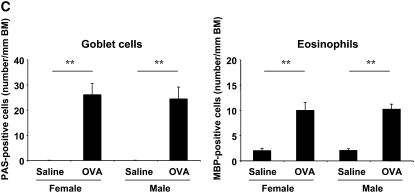
Figure 1.
Comparison of airway responsiveness and inflammation in female and male mice after 10-day ovalbumin (OVA) inhalation. Female and male mice were exposed to either a 0.9% saline solution or a 1% OVA solution for 10 days (20 min/d). (A) Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) to inhaled methacholine (MCh) after 10-day OVA inhalation. AHR (airway resistance [RL] and lung dynamic compliance [Cdyn]) to inhaled MCh was assayed 24 hours after the last OVA challenge. Circles, female mice; squares, male mice; open symbols, 10-day saline; solid symbols, 10-day OVA. (B) Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell composition after 10-day OVA inhalation. BAL fluid was recovered immediately after the AHR assay was completed. (C) Numbers of periodic acid-Schiff–positive and major basic protein–positive cells. Results represent the mean ± SEM (n = 8). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus 10-day saline exposure in each sex. ND = not detected. The baseline values of RL and Cdyn were as follows: 0.57 ± 0.03 cm H2O/ml/second (n = 16) and 0.069 ± 0.003 ml/cm H2O (n = 16) in female saline-treated mice, respectively; 0.59 ± 0.03 cm H2O/ml/s (n = 12) and 0.070 ± 0.002 ml/cm H2O (n = 12) in female OVA-treated mice, respectively; 0.55 ± 0.02 cm H2O/ml/second (n = 16) and 0.065 ± 0.003 ml/cm H2O (n = 16) in male saline-treated mice, respectively; 0.57 ± 0.02 cm H2O/ml/second (n = 21) and 0.064 ± 0.003 ml/cm H2O (n = 21) in male OVA-treated mice, respectively. BM = basement membrane.