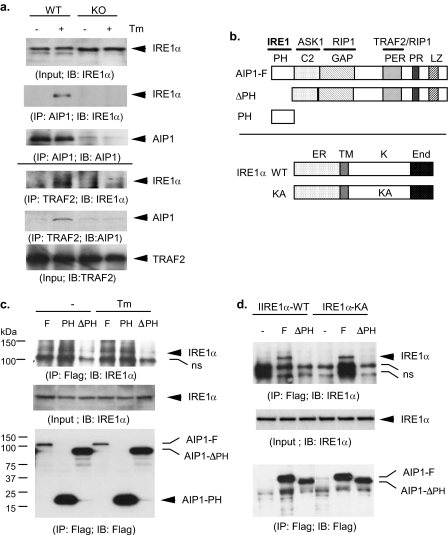
FIGURE 3.
ER stress induces formation of AIP1-IRE1 complex, and the PH domain of AIP1 is critical for the RE1 binding. a, ER stress-induced formation of endogenous AIP1-IRE1-TRAF2 complexes in EC. MLEC were treated with Tm (1 μm for 15 min). Association of AIP1 with IRE1 was determined by immunoprecipitation with AIP1 followed by Western blot with anti-IRE1 or anti-AIP1 (top three panels). Association of TRAF2 with IRE1 and AIP1 was determined by immunoprecipitation assay with anti-TRAF2 followed by Western blot with anti-IRE1 or anti-AIP1 (bottom three panels). b, schematic diagram for AIP1 and IRE1α structure domains and expression constructs. AIP1 contains a PH, a C2, and a GAP domain at the N-terminal half and a Period-like (PER) domain, a proline-rich (PR) region, and leucine-zipper (LZ) motif. The specific domains responsible for protein interactions with IRE1, ASK1, TRAF2, and RIP1 are indicated. IRE1α WT contains the ER lumen domain (ER), the transmembrane domain (TM), the kinase domain (K), and the endonuclease domain (End). KA, K599A. c, BAEC were transfected with FLAG-tagged AIP1-F, AIP1-ΔPH, or AIP1-PH in the presence of IRE1-WT. Cells were treated with Tm (1 μm for 15 min), and association of AIP1 with IRE1 was determined by immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG followed by Western blot with anti-IRE1. d, BAEC were transfected with FLAG-tagged AIP1-F or AIP1-PH in the presence of IRE1-WT or IRE1-KA. Association of AIP1 with IRE1 was determined as in c. ns in c and d, nonspecific band.