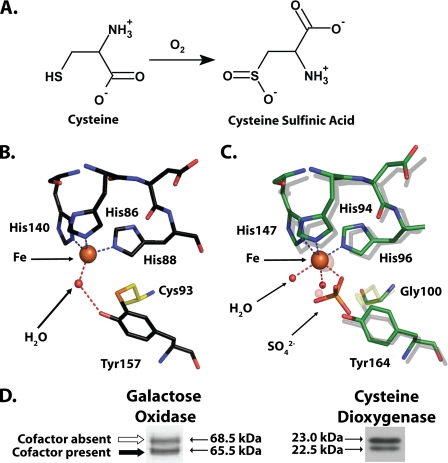
FIGURE 1.
A, reaction catalyzed by CDO. B, cutaway view of the rat CDO active site (PDB entry 2B5H (16)), showing the cross-linked amino acid cofactor composed of residue Cys93 covalently bound to Tyr157. Also visible is the iron cofactor of CDO and a single molecule of water hydrogen bonded to the iron and Tyr157. C, superimposition of select active site residues from a bacterial CDO (C. necator, indicated by a green carbon backbone; PDB entry 2GM6) and rat CDO (indicated by a gray carbon backbone). The indicated residue numbers are for C. necator. Note that C. necator CDO is unable to form a cross-linked amino acid cofactor because it contains a glycine in the position where there is a cysteine in rat CDO. D, both galactose oxidase (modified from Fig. 2 of Whittaker and Whittaker (13)) and rat CDO (obtained from rat liver) run as a double band when analyzed by SDS-PAGE. In the case of galactose oxidase, the apparent migration difference is because of the presence of a thioether-containing cross-linked cofactor in the bottom band and its absence in the top band (13).