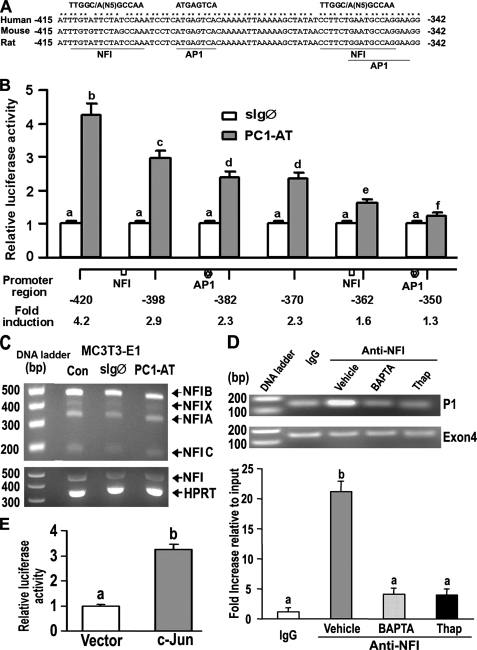
FIGURE 7.
NFI and AP-1 transcription factors mediate PC1-dependent activation of the P1 Runx2-II promoter. A, schematic showing two NFI and AP1 binding sites located between -415 and -342 region of the Runx2-II P1 promoter that are conserved across species. B, assessment of NF1 and AP1 function by deletion analysis of the Runx2 P1 promoter. MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts were transiently co-transfected with PC1-AT or sIgØ along with Runx2-P1 promoter-luciferase constructs that contained successive 5′ deletions. Loss of NFI and AP1 sites resulted in a progressive reduction in PC1-mediated stimulation of Runx2 P1 promoter activity. C, RT-PCR analysis of NFI-A, -B, -C, and -X isoform expression in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts transiently transfected with either the control sIgØ or the PC1-AT constructs for 48 h. Neither PC1-AT nor sIgØ increased NFI message levels above untransfected controls (CON) in MC3T3-E1, raising the possibility that PC1 regulates NFI through post-translational modifications. HPRT, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. D, quantitative ChIP analyses demonstrating specific interaction of NFI with Runx2-II P1 promoter. Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using set of primers indicated under “Experimental Procedures.” The upper panel is a representative ethidium bromide gel of PCR products, and the lower panel is bar graph representing mean ± S.E. from at least three independent experiments. Values are shown as relative -fold of enrichment of the promoter sequence normalized for coding region sequence versus that obtained for input samples. Values sharing the same superscript (a, b, c, and d) are not significantly different at p < 0.05. Immunoprecipitations were performed with NFI antibody or with normal rabbit IgG as described under “Experimental Procedures.” E, transient co-transfection c-Jun plasmid with Runx2 P1-420-Luc (p0.42Runx2P1-Luc) stimulated Runx2 P1 promoter activity, consistent with functional AP-1 binding sites.