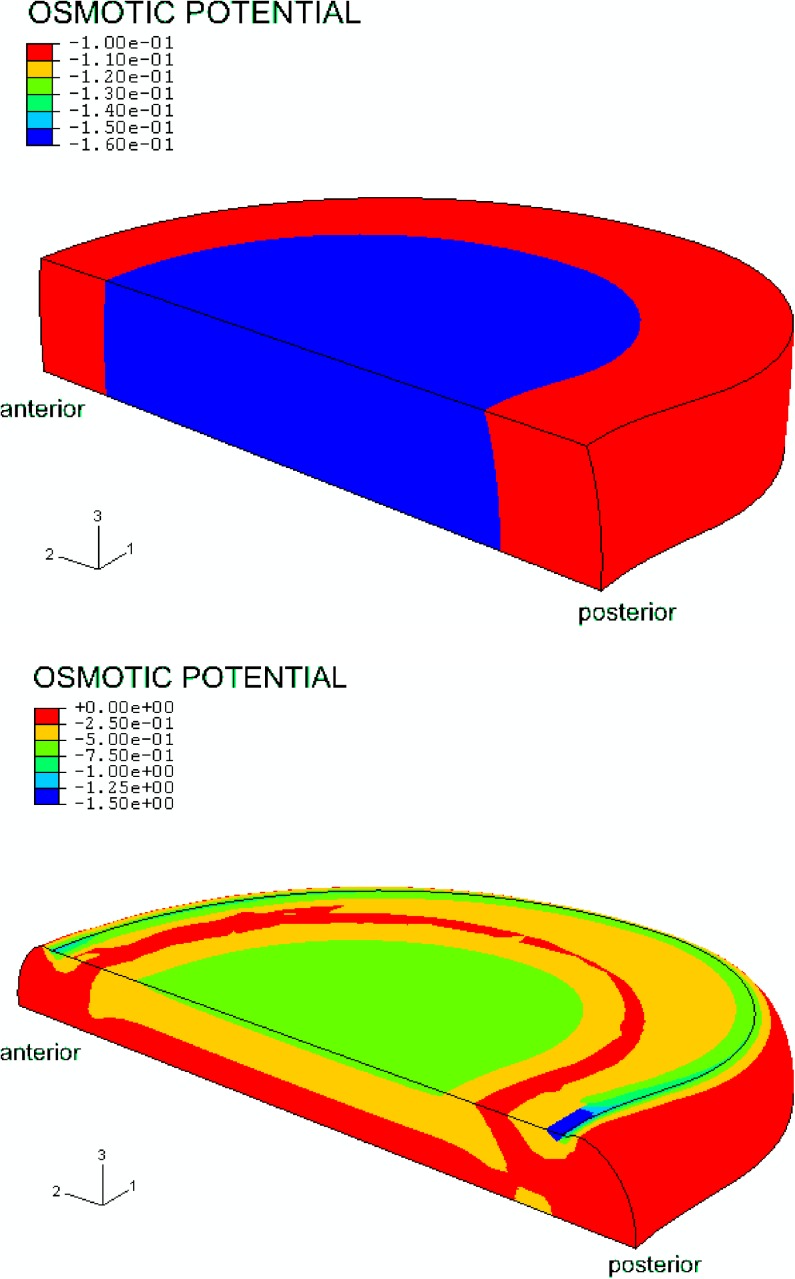
Fig. 5.
Color plot of an unloaded model (top) and an axially loaded model with 1,000 N (bottom), showing the osmotic potential (the negative of the osmotic pressure). After swelling, during the first step, osmotic pressure is highest in the nucleus pulposus, while the osmotic pressure in the annulus is about 40% lower. After loading, the osmotic pressure rises first close to the outflow boundaries. When the fluid is pressed out, the fixed charge density concentration increases, which results in an increase of osmotic pressure