Figure 2. Klf5 is induced in response to infection with C. rodentium.
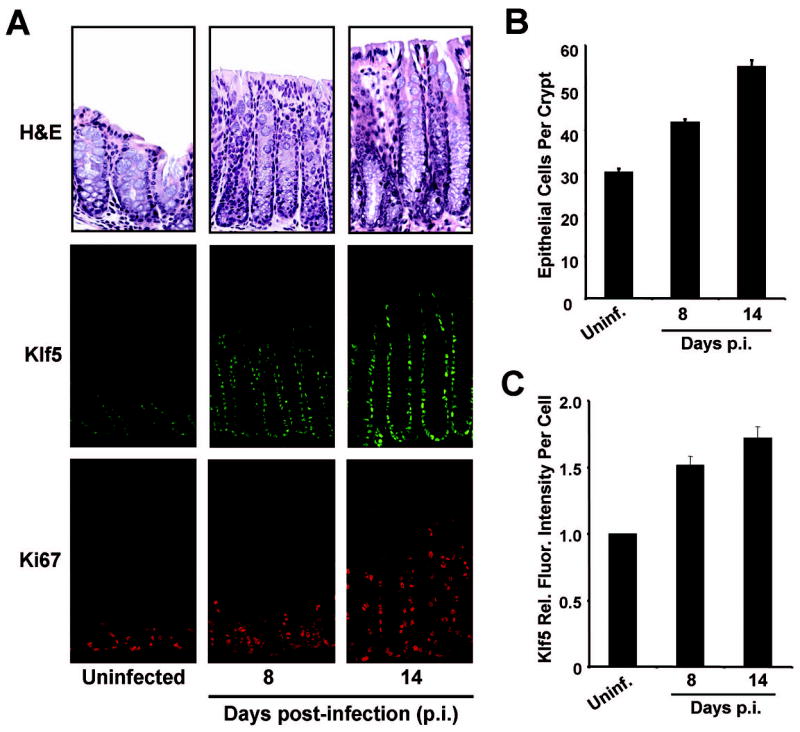
Frozen tissue sections from distal colon were isolated from mice given PBS (uninfected) or infected with C. rodentium and sacrificed 8 or 14 days post-infection (p.i.). (A) Tissues were stained with H& E, or for immunofluorescence using antibodies derived against Klf5 (green) or Ki67 (red). (B) The numbers of epithelial cells per crypt in colons of uninfected or infected mice were measured on the H&E sections. Five crypts per sample were counted. (C) Relative immunofluorescence intensities for Klf5 were determined on a per cell basis by quantitative analysis of Klf5 immunofluorescence images. For each condition, at least 200 cells positive for Klf5 expression were quantified for average fluorescence intensities.
