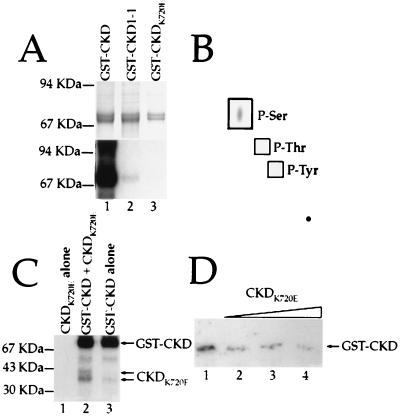
Figure 3.
Autophosphorylation of the CLV1 kinase domain. (A) GST fusion-proteins containing the wild-type (lane 1), CLV1-1 (lane 2), and CKDK720E (lane 3) forms of the CLV1 kinase domain were allowed to phosphorylate in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. (Upper) The Coomassie blue-stained gel showing the relative amounts of fusion protein in each lane. (Lower) The autoradiograph. (B) The wild-type CLV1 kinase domain was allowed to autophosphorylate, then hydrolyzed. The products of the hydrolysis reaction were analyzed by electrophoresis on a TLC plate. Only serine residues were phosphorylated. (C) Autophosphorylation reactions containing CKDK720E alone (lane 1), CKDK720E plus GST-CKD (lane 2), and GST-CKD alone. (D) Increasing amounts of CKDK720E protein were added to a constant amount of GST-CKD during autophosphorylation reactions. The approximate molar ratios of CKDK720E:GST-CKD are 0:1 (lane 1), 1:1 (lane 2), 2:1 (lane 3), and 4:1 (lane 4). Arrow shows the position of the full length GST-CKD protein.