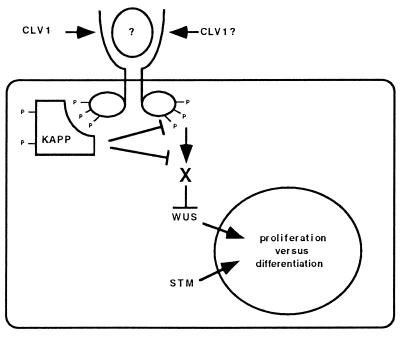
Figure 5.
Model of CLV1 and KAPP Action. The model predicts that CLV1, upon binding a peptide ligand, dimerizes and allows intermolecular phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic kinase domains. The activated receptor then binds and phosphorylates KAPP. The KAPP protein may then modify the CLV1 signal by directly dephosphorylating CLV1. The CLV1 kinase domain probably interacts with other positively acting components (X), which may or may not be dephosphorylated by KAPP. Based on epistasis analysis, WUS may function downstream of CLV1 to promote cell divisions. SHOOTMERISTEMLESS may function independently but competitively with the CLV1 signaling pathway to promote cell division (24).