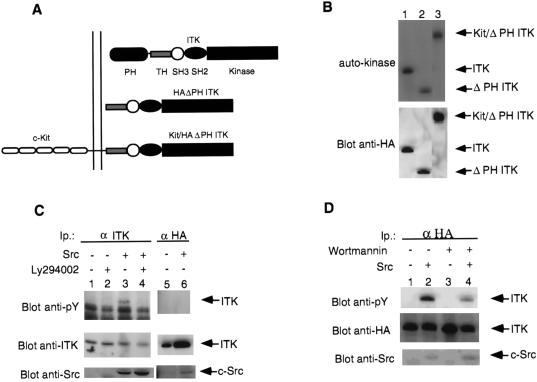
Figure 1.
Structure of the different ITKs used in this study. (A) HAΔPH ITK: HA-tagged PH-deleted ITK; Kit/ΔPH ITK: murine c-Kit/HAΔPH ITK fusion. (B) Expression and kinase activity of ITK and mutants. Immunoprecipitates of ITK or mutants from transfected COS-7 cells were analyzed for autokinase activity (Top). Lanes: 1, ITK (wild-type); 2, ΔPH ITK; 3, Kit/ΔPH ITK. (Bottom) Probed with anti-HA. Arrows point to wild-type ITK or the mutants. (C) Tyrosine phosphorylation of ITK in the presence of Src and inhibition by Ly294002. COS-7 cells transfected with untagged wild-type ITK (except for lanes 5 and 6, where HA-tagged wild-type ITK was used) in the presence or absence of wild-type or kinase-inactive (K295M) c-Src as indicated. ITK immunoprecipitates were analyzed for enzymatic activity (see Fig. 2A) or phosphotyrosine (Top). Lanes 1, 2, and 5 contain ITK without c-Src; lanes 3, 4, and 6 contain ITK with c-Src. Lane 6 contains ITK cotransfected with the kinase-inactive c-Src. Lanes 2 and 4 were from cells incubated with Ly294002. (D) Inhibition of Src-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of ITK by wortmannin. COS-7 cells transfected with untagged wild-type ITK in the presence or absence of wild-type c-Src as indicated. ITK was immunoprecipitated and analyzed for phosphotyrosine (Top). Lanes: 1 and 3, ITK without c-Src; 2 and 4, ITK with c-Src. Lanes 3 and 6 were from cells incubated with wortmannin. Probes: (C and D Top) anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies; (Middle) anti-ITK antibodies; and (Bottom) anti-Src antibodies on whole cell lysates. Arrow indicates ITK or c-Src.