Figure 5. Heterosynaptic induction of TA–CA3 LTP by MF inputs.
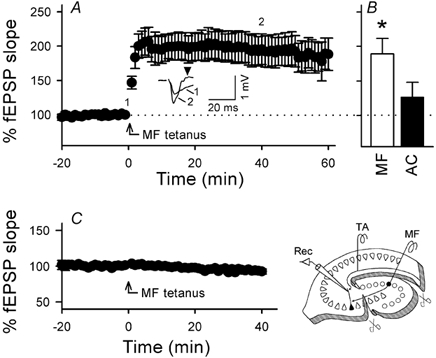
A, time courses of TA–CA3 responses following MF tetanization (100 Hz for 1 s). The tetanus was applied without TA stimulation. TA-evoked fEPSPs gradually increased up to about 200 % and were maintained for at least 60 min. Representative traces at times 0 and 40 min are shown in the inset. After MF tetanus, a TA stimulus that was previously ineffective to evoke a spike elicited spike-relevant responses (arrowhead) in most cases tested (> 90 %), which suggests that MF activation gates TA inputs. B, the average fEPSP slopes from 40 to 60 min after tetanic stimulation of MF (white column, n = 6) or AC (black column, n = 6). A significant increase in TA-evoked fEPSPs was obtained only for MF tetanization. C, in stratum lucidum-transected slices (as shown in the schematic drawing), MF tetanization (100 Hz for 1 s did not cause the induction of heterosynaptic LTP (n = 4). Data represent means ± s.e.m. of n cases.
