Figure 6. Effects of i.c.v. administration of melatonin on light-induced GVNA responses.
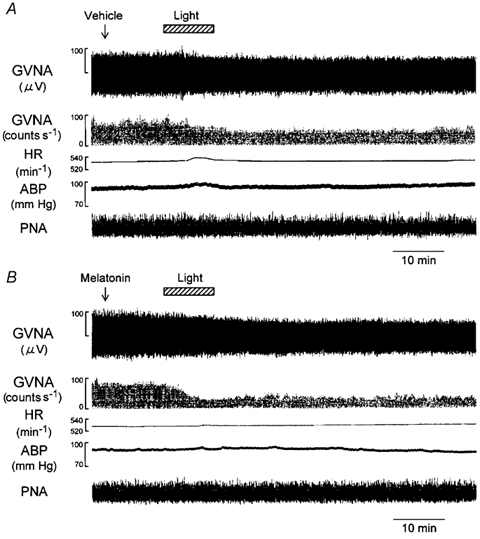
Traces in A and B show examples of the effects of light (2.1 × 1014 photons cm−2 s−1, 10 min) on GVNA, event counts of the GVNA, HR, ABP and PNA following i.c.v. injection of vehicle (A) or melatonin (0.1 ng; B). The light-evoked GVNA suppression was greater in melatonin-administered mouse than in the vehicle-administered mouse.
