Figure 1. Activation of 5-HT receptors induces heterogeneous effects in spinal motoneurons.
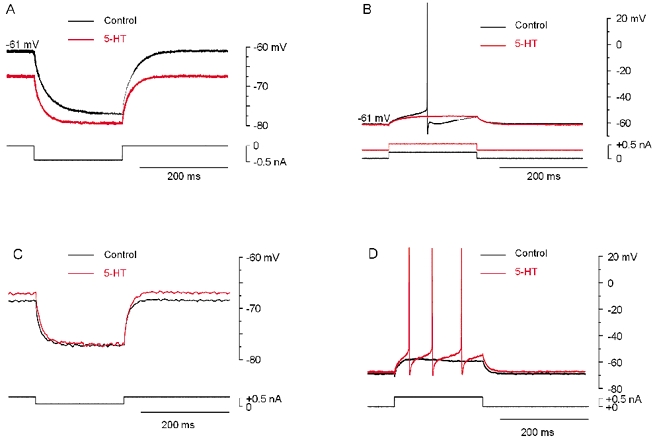
A, response of a motoneuron to a hyperpolarizing current pulse before (black trace) and after addition of 5-HT (10 μm; red trace). 5-HT hyperpolarized the cell from −61 to −68 mV and decreased the input resistance from 32 to 25 MΩ (−21.9 %). B, response to positive depolarizing current pulses. In 5-HT (red), a positive bias current was injected in the cell to adjust the membrane potential to the same value as in control. Note the decrease in excitability. C, response of another motoneuron to hyperpolarizing current pulses. 5-HT (red) depolarized the cell from −70 to −68 mV and increased the input resistance from 18 to 20 MΩ (+11.1 %). D, response to positive depolarizing current pulses. Note the increase in excitability induced by 5-HT (red). No bias current was injected. A and B from one motoneuron, C and D from another motoneuron. In all experiments synaptic potentials were blocked by CNQX (25 μm), AP7 (25 μm) and strychnine (10 μm).
