Figure 7. The effects of [Cs+]o and [K+]o on the voltage dependence of τinact of outward Cs+ current recorded with 130 mm Cs1+.
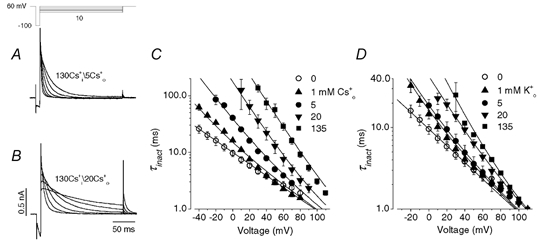
A and B, HERG Cs+ currents elicited by the voltage protocol shown above the current traces in external solution containing 5 mm Cs0+ (A) or 20 mm Cs0+ (B). HERG channels were initially inactivated at the holding potential of +60 mV. As with data in Fig. 4, a 10 ms repolarizing step to −100 mV allows HERG channels to recover from inactivation, and steps to a range of test potentials allows the inactivation time course to be observed. C, voltage dependence of time constant of the decay of outward Cs+ current at different [Cs+]o. Data were fitted (continuous lines) to eqn (5). Cs0+ increased τinact and modulated the voltage sensitivity of the τinact−V relationship. The free parameters for each fit are shown in Table 1. The mean Kd(0) and δ values are 1.7 ± 0.2 mm and 0.66 ± 0.05, respectively (n = 4). D, as in C, but with varying [K+]o. The mean Kd(0) and δ values are 6.8 ± 2.8 mm and 0.63 ± 0.04, respectively (n = 4). Thus, with Cs0+ and K0+ the location of the binding site in the electrical field is similar but the affinity of the site for K+ is slightly lower.
