Figure 5. Effect of local microapplication of high [K+].
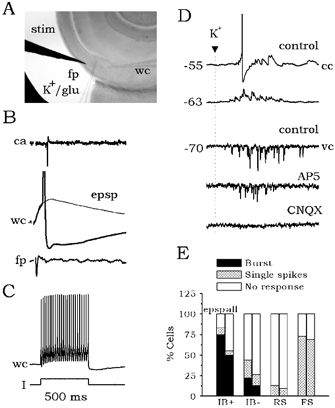
A, schematic of the experimental design used in the microapplication experiments. The stimulating (stim) and the whole-cell (wc) electrodes were left fixed. Once an FS interneuron was recorded, the field potential electrode (fp) was replaced by a pipette filled with either 145 mm KCl or 0.5 mm glutamate (K+/glu). Local drops of these solutions were then applied. B, typical response of an FS cell (C) to local excitation elicited by antidromic activation of projection cells. D, local drops of high K+ caused a barrage of glutamatergic synaptic events at different membrane potentials as recorded in current- (cc) and voltage-clamp (vc) modes. Similar results were obtained with microapplication of glutamate. The EPSC barrage evoked by microapplication of high K+ was blocked by CNQX but not by AP5. E, effect of local inhibition in the responsiveness of distinct cell types to local excitation.
